Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
LED lighting technology has become a revolutionary force in modern lighting solutions. Offering significant energy savings, superior brightness, and longer lifespans compared to traditional lighting methods, LED (Light Emitting Diode) lights have gained widespread popularity in homes, industries, and outdoor environments. But how are LED lights made, and what are the materials involved in the production process?

What are LED Lights Made of?
LED materials include LED chips, phosphors, substrates, radiators, circuit boards, electronic components, housings, reflectors, lenses.
Light Source
The light source in an LED is the LED chip, which is responsible for producing light. The chip is placed on a substrate and encapsulated with a phosphor coating (in the case of white LEDs) to modify color of the emitted light.
Drive and control
The LED driver is an essential component that regulates the electrical current and ensures that the correct amount of power is delivered to the LED chip. It converts AC (alternating current) from a power source into DC (direct current), which is required by LEDs to operate.
Heat Dissipation
Excessive heat can degrade the performance of LED chips and reduce their lifespan. Heat sinks, usually made of aluminum, are used in LED lights to draw heat away from the LED chip and disperse it safely. There is also thermal grease to fill gap between chip and radiator to improve heat conduction efficiency.
Structure and optics
A lens/reflector is often used in LED lights to control distribution of light, focusing or diffusing it based on application. Lenses are typically made of durable materials such as glass or plastic and are designed to enhance the performance and efficiency of the LED by directing the light where it is needed.
The LED lights housing made of die-cast aluminum or plastic, integrates all components and protects the light.
LED light material complete table:
| Component | Function | Common Materials / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| LED Chip (Emitter) | Converts electrical energy into light | GaN / InGaN / GaAs semiconductor materials |
| Phosphor | Converts blue/UV LED light to white or other color temperatures | YAG:Ce, silicate-based phosphors; applied as coating |
| Substrate / PCB | Mechanical support and thermal path for the chips | Aluminum PCB, copper PCB, ceramic substrates |
| Heat Sink / Thermal Management | Dissipates heat to maintain performance and lifetime | Aluminum extrusion/die-cast, copper, thermal interface materials |
| Driver / Power Supply | Converts mains to constant current/voltage for LEDs | ICs, capacitors, inductors; enclosed in plastic or metal housing |
| Lens / Optics | Controls light distribution and beam angle | PMMA (acrylic), PC (polycarbonate), glass |
| Reflector / Secondary Optics | Improves light uniformity and directs lumen output | Al-coated plastics, anodized aluminum |
| Housing / Enclosure | Protects internal parts and provides mounting | Aluminum, steel, PC/ABS plastics; powder coat or anodize finish |
| Seals & Gaskets | Provides ingress protection and vibration resistance | Silicone, EPDM rubber, polyurethane potting |
| Connectors & Wiring | Electrical connection between driver, LED, and mains | Copper wires, terminal blocks, solder joints, wire harnesses |
How Are LEDs Made?
The process of LED manufacturing involves multiple steps, from the preparation of semiconductor wafers to the final assembly of the lighting product. Here’s an overview of how LED lights are made.
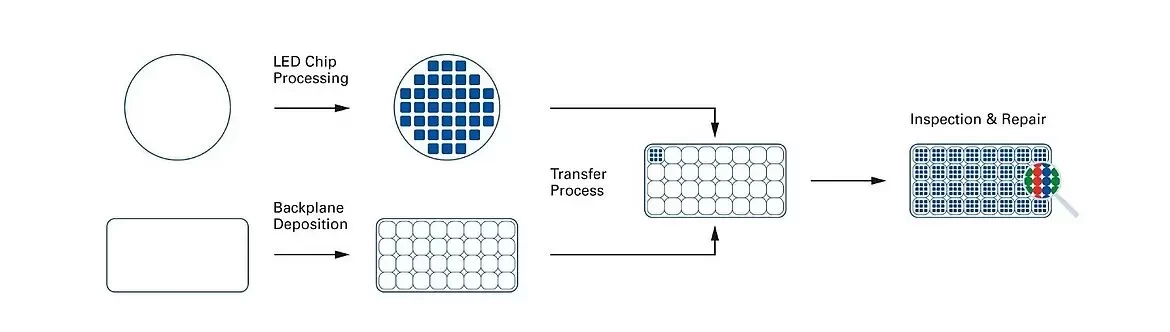
- Semiconductor Material Preparation
The first step in LED manufacturing is the preparation of the semiconductor material, typically gallium nitride (GaN) or gallium arsenide (GaAs). These materials are used to create the semiconductor wafers, which are sliced into thin layers. - LED Chip Fabrication
The semiconductor wafers are then processed to create LED chips. The process involves:
Doping: Introducing impurities into the semiconductor material to create p-type and n-type regions, which are essential for the diode function.
Etching: Creating the light-emitting surface of the LED chip. - Phosphor Coating
For white LEDs, a phosphor coating is applied to the LED chip. The phosphor converts the blue or ultraviolet light emitted by the LED chip into a broad spectrum of visible light, typically white. - Assembly of Components
The LED chip is mounted onto a substrate and connected to the driver, heat sink, and other essential components. The lens is then added to control the distribution of the emitted light. - Testing and Quality Control
After assembly, each LED is tested for performance, including brightness, color accuracy, and energy efficiency. Strict quality control measures ensure that the final product meets the necessary standards.
What is the Process Flow of LED Manufacturing Facility?
R&D and Design
The process begins with research and development (R&D), where engineers design new LED products and optimize existing designs for improved performance. Innovations may include advancements in semiconductor materials, LED chip designs, and heat dissipation techniques.
Laboratory Research
In the laboratory, scientists conduct material analysis and performance testing on LED chips to optimize luminous efficiency and ensure the highest quality of light output. The goal is to increase the reliability of the semiconductor wafers and the longevity of the final LED product.

Tooling and Machinery Manufacturing
In this stage, tooling machinery is developed for use in the LED production process. Specialized machines are designed to fabricate the semiconductor wafers and other components required for assembling LEDs.

Polyester Molding Machine and Foaming Equipment
Polyester molding machines are used to encapsulate the LED chips in protective material, providing moisture resistance and shielding them from environmental factors. This step is essential in ensuring the durability and reliability of the final product.
Component Assembly
The LED chips are carefully assembled with other components, including the heat sink, driver, and lens. This process ensures that the LED lights function properly and are ready for use in various applications.

Testing and Quality Control
After assembly, each LED light undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets performance and safety standards. This includes tests for:
- Luminous efficiency
- Electrical performance
- Heat dissipation
- Waterproofing and environmental resistance
Summary
LED lighting technology represents a significant leap forward in energy-efficient lighting solutions. By understanding what LED lighting is made of and the process flow of LED manufacturing, it’s clear that the production of LED lights involves cutting-edge technology, precision engineering, and advanced materials like semiconductors.
Ledrhythm has a complete LED lighting manufacturing system. View our quality control and company information. Feel free to contact us to customize your LED lighting solution.
People Also Ask
How does an led produce light?
The principle of LED light emission is that when current passes through a PN junction made of semiconductor material, electrons and holes recombine in the junction area and release energy. This energy is emitted in the form of photons, thereby generating visible light or light in other bands.
- Semiconductor PN: The fundamental structure of luminescence.
- Electron-hole recombination: The physical process by which luminescence occurs.
- Energy released as photons: Energy converted into light during recombination.
- Electroluminescence: The direct conversion of electrical energy into light.
What are LED materials used to make lights?
LED lights are mainly composed of LED chips, packaging materials, drive circuits, heat sinks, lenses and casings.
Is the LED manufacturing process complicated?
Yes. The LED manufacturing process is indeed complex and technically challenging, involving a variety of precision processes, such as semiconductor physics, materials science, thermodynamics, and optical engineering.











