Table of Contents
Toggle1. Introduction
LED dimming technology, particularly 0-10V dimming, is transforming the way we use lights in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
In this article, we’ll explore how dimmable LED lights, controlled via various switches like dimmer switches for LED lights with remote, dimmable LED strip lights, and dimmer 5modules, work.
We’ll also dive into whether all lights can be dimmed and how to address common dimming issues like flickering, buzzing, and compatibility. Whether you’re looking for dimmable LED lighting fixtures or trying to understand how 0-10V dimming fits into your existing system, this guide has you covered.
2. What is 0-10V Dimming?
Okay, so what’s the deal with 0-10V dimming? The name may sound technical, but it’s actually a simple way to control how bright or dim your lights are. Imagine it like a volume knob for your lights.
Instead of sending full power to your lights all the time, this system sends a voltage signal—anywhere between 0 and 10 volts. When the signal is at 10 volts, your lights are at full brightness. At 0 volts? They’re off, or nearly off, depending on the setup.
Here’s how it works in a nutshell:
- 0-10V dimmer switch: This is what you’ll use to turn the light’s intensity up or down.
- 0 10v wiring: These are the wires that carry the signal from the dimmer to the light fixture.
- Multiple fixtures, one control: You can dim several lights at once, making it ideal for larger spaces like offices, warehouses, or even cozy home theaters.
| Dimming Technologies Compared | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimming Method | Voltage Control | Applications | Benefits | Downsides |
| 0-10V Dimming | 0-10 volts | Commercial/Industrial | Precise control, reliable | Needs specific wiring |
| Line Voltage Dimming | 120-277 volts | Residential/Commercial | Easy setup, affordable | Less fine control, may flicker |
| DC Light Dimming | Low voltage | LED strips, small lights | Energy-efficient, compact | Limited to low-power applications |
3. Benefits of LED Dimming
More to dimmable LED bulbs exists than just mood lighting. Let’s talk about the real perks:
- Energy efficiency: When you dim the lights, you reduce brightness and use less electricity. Some studies suggest you can save up to 80% in energy use just by dimming your lights.
- Extended lights longevity: Dimming your lights can notably prolong their life expectancy. Less intensity means less wear and tear on the lights, so you won’t need to change them as often.
- Regional adaptability: Different areas require different brightness, such as different work areas in a factory. 0-10V dimming can be adjusted to the best lighting experience at any time.
- Comfort and ambiance: Whether you’re hosting a dinner party or relaxing with a book, dimming gives you the flexibility to set the perfect atmosphere. Plus, with options like remote dimmer switches for LED lights, you don’t even have to get off the couch to change things up.

4. How Does a 0-10V Dimming System Work?
Here’s where we get into the nitty-gritty. 0-10V dimming works by sending a control signal to your lights that varies between 0 and 10 volts.
This signal controls the brightness. Ten volts means full brightness, while zero volts turns the lights off. It can also dim the lights to the lowest setting allowed.
- Dimmer switch: This is what you’ll adjust to control the voltage.
- Wiring: The 0 10v dimmer wiring carries the voltage signal to the light fixtures.
- LED drivers: These guys regulate the voltage and make sure the lights get the correct current without flickering or buzzing.
Diagram: Diagram for a 0-10V Dimming System:
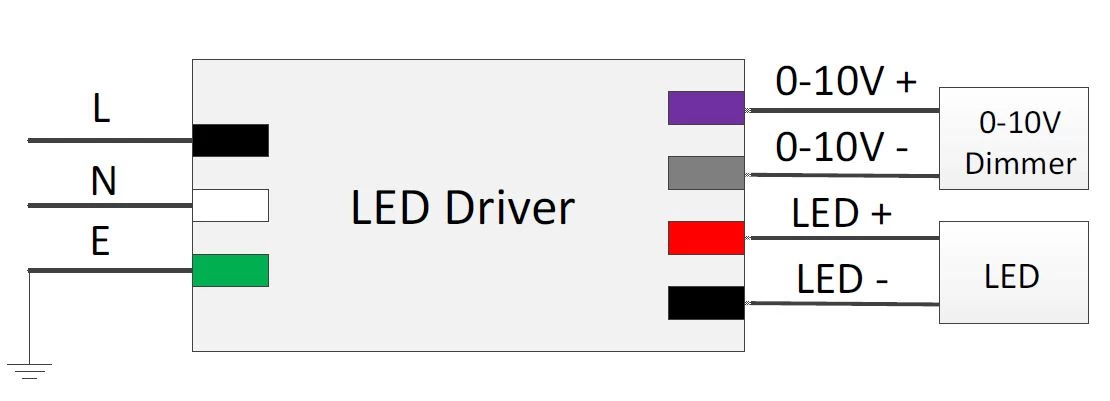
4.1 0-10V Dimming Wiring Methods
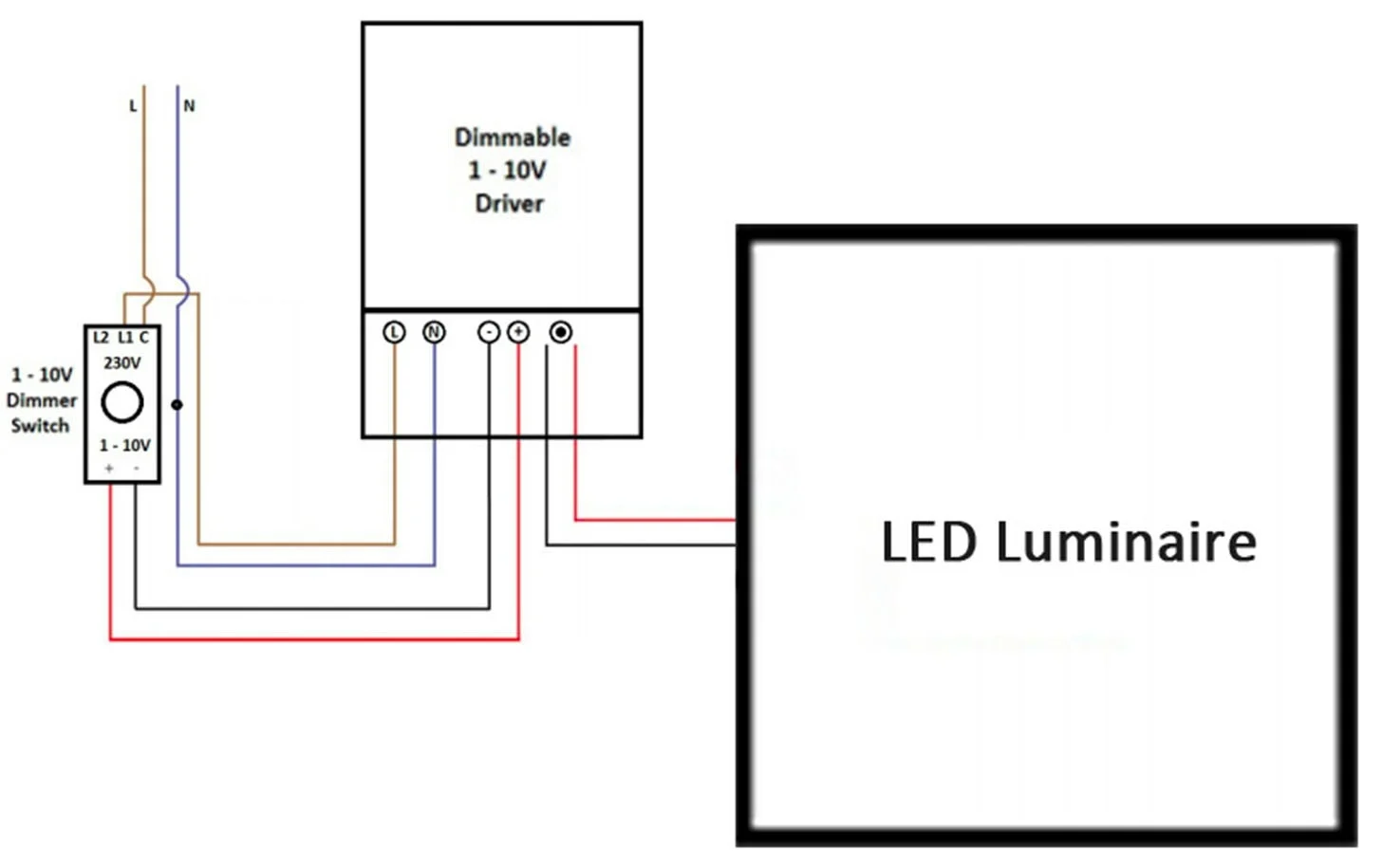
The wiring of 0-10V dimmer is actually very simple. Once you learn it, you can operate and maintain it yourself.
- Main Power Connection:
Connect the L (Live) and N (Neutral) wires of the AC power supply to the dimming power input. - LED Output Connection:
Connect the LED output (positive and negative) of the LED driver to the luminaire input. - Dimmer Control Cable Connection:
Connect the +V and -V signal wires of the dimmer to the dimming input of the LED driver (labeled “DIM+” and “DIM-” or “0-10V+ / 0-10V-“).
Note:
- Do not connect the polarity incorrectly: +V and -V must be correctly aligned.
- Do not mix the 0-10V dimming cable with the power cable; these are low-voltage control cables and should be run in separate cable trays for safety.
- When dimming multiple luminaires in series, DIM+ and DIM- can be used to connect multiple drivers in parallel for unified control.
0-10V Dimmer Wiring Diagram:
5. Advantages of 0-10V Dimming
There are plenty of reasons why 0-10V dimming is a solid choice:
- It’s adaptable: Works with a wide range of lighting, from low voltage LED dimmers to high wattage dimmable LED bulbs.
- Smart system integration: Want to control your lights via a smart home setup? No problem. Many 0-10V dimming systems play well with remote dimmer switches and other smart tech.
- Smooth dimming: No one likes flickering lights, and 0-10V dimming is known for delivering a continuous, flicker-free experience.
6. Disadvantages of 0-10V Dimming
But, as with anything, 0-10V dimming isn’t perfect:
- More complex installation: It requires specialized wiring, so if you’re retrofitting a space, this might be more hassle than it’s worth.
- Costs: The extra components and wiring can make it pricier to install upfront.
- Not every light works: Some bulbs, especially older or non-dimmable lights, won’t play nice with a 0-10V dimming system.If your LED lights flicker, an incompatible dimmer may be the cause.
7. Can Any Light Be Dimmable?
Unfortunately, no. If you have LED lights with on/off switches or non-dimmable bulbs, trying to dim them can cause problems. You might see flickering or hear buzzing. It could even shorten the bulb’s life.
That’s why it’s important to make sure your LED light bulbs, LED strips, or lighting fixtures are actually labeled as dimmable before installing them in a dimming system.
8. Can I Use My Existing Dimmer to Dim LED Light Bulbs?
If you’ve recently switched to LED lights but still have the old dimmer from your incandescent bulbs, you might notice some issues. Many traditional dimmers were not made for LED dimmer bulbs.
This can cause issues like a limited dimming range or a buzzing sound. The best move? Upgrade to an LED-compatible dimmer switch, like a 0 10v dimmer, for a smoother experience.
9. Steps to Dimmable LED Synchronizing with Other Devices
To get the most out of your dimmable LED setup, here’s what you’ll need:
- Switches: Ensure you’re using a dimmer switch for LED lighting that’s built for your system, whether it’s a basic switch or a dual switch dimmer LED.
- Sensors: Incorporating motion or smart sensors can sync your lighting with room activity.
- Remotes: Adding a remote control dimmer for LED lights can give you added convenience.
| Different Types of Dimmer Switches and Their Uses | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimmer Type | Best For | Key Features | Limitations |
| 0-10V Dimmer Switch | Commercial, industry,large spaces | Smooth, flicker-free dimming, precise brightness control | Requires separate control wiring |
| Remote Control Dimmer | Homes, smart lighting setups | Wireless operation, app or voice control | Dependent on batteries or network reliability |
| Low Voltage Dimmer Switch | LED strips, DC lighting fixtures | High precision, energy-efficient | Limited to low-voltage systems only |
| TRIAC/Phase-Cut Dimmer | Residential, retrofit applications | Compatible with standard wiring, cost-effective | May cause flicker or buzzing with incompatible LEDs |
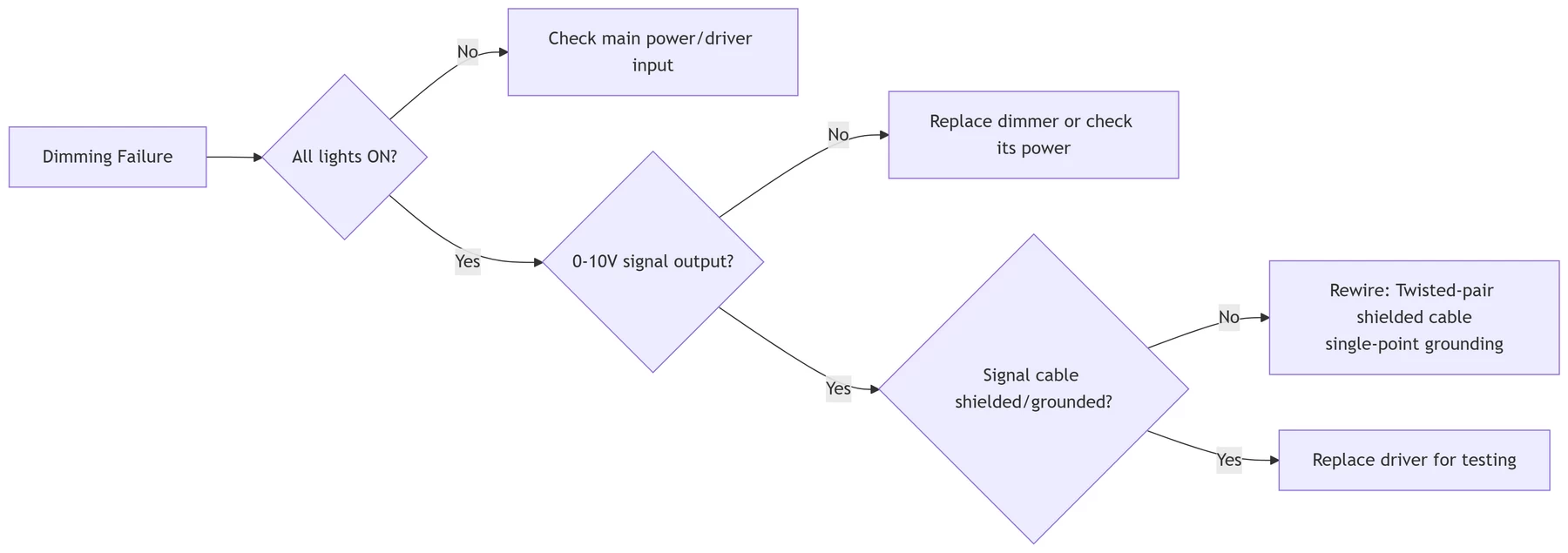
10. How to Solve Common Problems with 0-10V Dimming Systems
Even the best systems hit bumps along the way. Here’s how to solve a few common issues:
- Flickering lights: This usually happens if your dimmer switch and LED lights aren’t a good match. Make sure you’re using compatible components, like a 0 10v dimmer for your dimmable LED setup.
- Buzzing noises: This can be caused by dimmers that weren’t designed for LED lights.
- Compatibility issues: Always double-check that your LED dimmer bulbs or dimmable LED strips work with your dimmer switch to avoid performance problems.
- Dimming does not work: usually caused by wiring errors or incompatibility. Make sure the dimmer output (+10V, DIM-) corresponds to the driver interface. Use a multimeter to check the dimmer output voltage (normal range 0-10V).
11. LedRhythm’s 0-10V Dimming Lighting Products
Looking for reliable, high-quality 0-10V dimmable LED? LedRhythm has you covered. From our slimline floodlight series to LED high bays, we offer energy-efficient and durable solutions for industrial and commercial lighting needs—whether you’re looking for a shopping mall, sports stadium, office, or industrial space.View all our LED lighting products.

12. Conclusion
In a world where lighting can make or break the atmosphere of a room, 0-10V dimming stands out as a game-changer. With the right system, you can easily control light levels, reduce energy usage, and extend the lifespan of your bulbs. Whether you’re using a high wattage LED dimmer switch or a remote dimmer, the possibilities are endless. And with LedRhythm’s range of dimmable LED products, you can take your lighting setup to the next level.
13. People Also Ask
Is 0-10V dimming a must in modern LED lighting?
0-10V dimming is common in LED lighting, but not essential. It’s a widely used analog dimming technology, particularly suitable for commercial and industrial lighting (such as offices, warehouses, and retail spaces). It uses a 0-10V DC voltage signal to achieve smooth dimming, saving energy and reducing costs.
However, compatibility issues (such as inconsistent dimming due to inconsistent standards) and the need for additional control wiring make it not mandatory for all scenarios. Other dimming solutions are available on the market, such as DALI, PWM, and TRIAC, offering flexibility based on needs.
Why is 0-10V dimming commonly used in industrial and commercial LED lights?
0-10V dimming is commonly used in industrial and commercial lighting due to its strong compatibility, stable control, simple wiring, and low cost. It is particularly suitable for scenarios where large areas and multiple lamps need to be uniformly controlled, such as high-bay lights, floodlights, and tri-proof lights. It can achieve precise and smooth brightness adjustment, improving energy efficiency and comfort.
Are 0-10V dimmers for different LED lights compatible?
Yes. The same 0-10V dimmer can control multiple different brands of lighting fixtures, as long as they are all marked as supporting 0-10V.
The same dimmer can also control different types of lighting fixtures, such as panel lights, downlights, and floodlights, as long as the drivers are all 0-10V.








