Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Lighting plays a pivotal role in modern life, from enhancing productivity to reducing energy consumption. This guide will compare LED lighting with traditional options like incandescent bulbs and fluorescent light. By the end, you’ll understand why LED lights are a superior choice for residential, industrial, and commercial use.
What Are LED Lights?
An LED (Light Emitting Diode) is a highly efficient semiconductor device that produces light through electroluminescence. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs, which generate light by heating a filament, LED lighting produces light with minimal heat.
In addition, LED lights have high luminous efficiency and more energy-efficient. You can refer to article about LED equivalent power. For a detailed breakdown of the materials used in LEDs, read What Is LED Lighting Made Of.
LED Lighting vs Fluorescent Tubes vs Incandescent
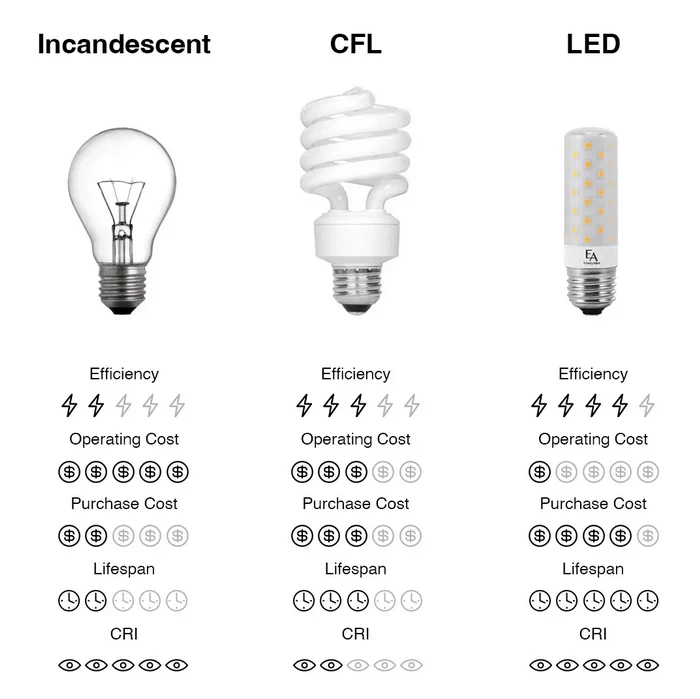
The greatest advantage of LED lighting lies in photoelectric conversion efficiency.
- Modern LEDs can convert 90% of electrical energy into visible light, typically achieving luminous efficacy exceeding 150 lm/W.
- Incandescent lights, which rely on a tungsten filament to generate heat, waste 93% of their energy as infrared radiation, with only 7% converted into light.
- While fluorescent lights are improvement over incandescent, they operate by first converting electrical energy into ultraviolet light, which is then converted to visible light through phosphors, resulting in a 40% energy loss. View about LED visible light.
| Specification | LED Light | Fluorescent Light | Incandescent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Luminous Efficacy (lm/W) | 80~200 | 40~70 | 8~15 |
| Lifespan (Hours) | 25,000~50,000 | 6,000~15,000 | 750~2,000 |
| Startup Time | Instant (< 0.1s) | 0.5~3s (with preheat) | Instant |
| Color Rendering Index (CRI) | 70~98 (90+ for premium) | 60~85 | 95~100 (Natural Light) |
| Heat Dissipation Ratio | < 20% | 40% | > 90% |
| Ultraviolet Radiation | None | Low (may contain UV) | Medium (mainly infrared) |
| Mercury Content | 0 mg | 3~5 mg/unit | 0 mg |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C (stable) | -10°C to +60°C (hard to start in cold) | Less affected by environment |
While LEDs have a higher initial cost, they have long lifespan and require less maintenance. They can significantly save on electricity costs, with a payback period of less than two years.
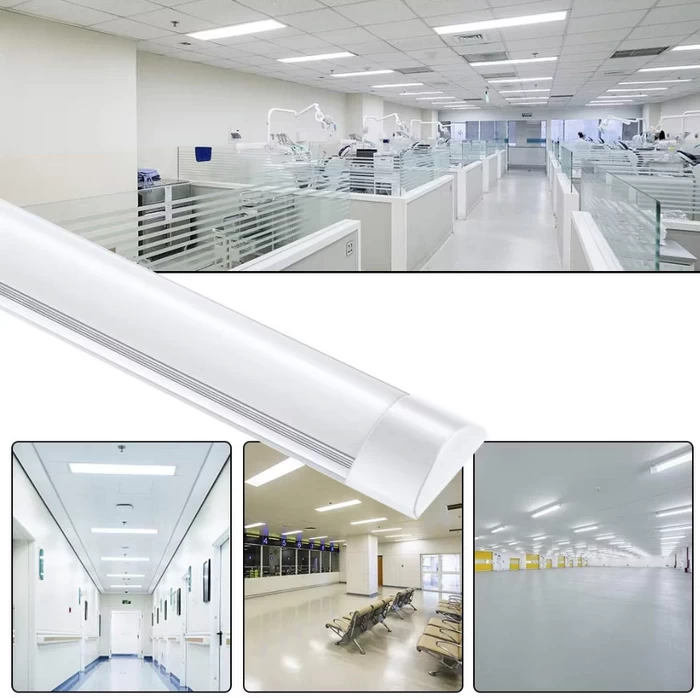

Replace Fluorescent Light With LED
The feeling of fluorescent light to led conversion is very obvious, with significant differences in user experience, lighting quality, and energy-saving efficiency. Especially in offices, commercial and homes, LED lighting has completely replaced fluorescent lights.
- LED lights turn on instantly, without any delay.
- LED lighting provides a more even, softer light, making it more comfortable to look at.
- At same brightness, LEDs typically consume half as much power as fluorescent lights or even less.
- LEDs can last for over 25,000 to 50,000 hours and withstand frequent on-off cycles.
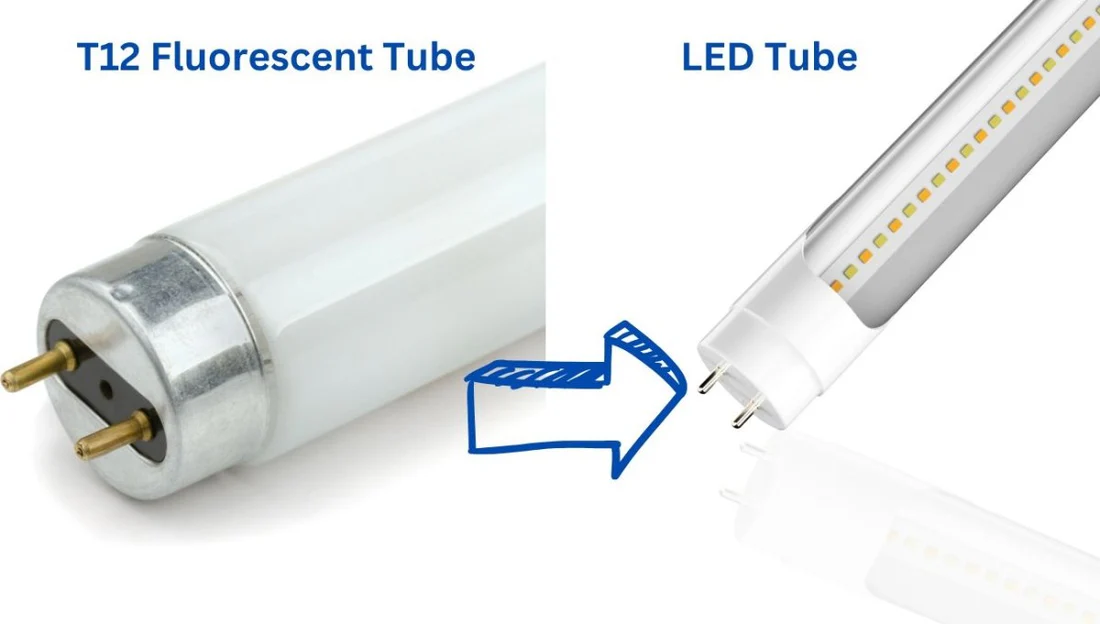

Lifespan and maintenance:
| Specification | LED Tubes | Fluorescent Tubes |
|---|---|---|
| Average Lifespan | 30,000 hours | 8,000 hours |
| Replacement Frequency | 5-7 years | 1-2 years |
| Ballast Failure | None | Average Annual Failure Rate: 15% |
Replacing fluorescent light fixture with led:
| Replacing Target | Key Points for LED Selection | Consequences of Incorrect Selection |
|---|---|---|
| T8 Fluorescent Tube | Length Matching (0.6m/1.2m/1.5m) | Installation Failure |
| High Bay Fluorescent Light | >10,000lm High Bay LED | Insufficient Illumination |
| Waterproof Fluorescent Light | IP65 Protection Rating | Moisture Intrusion Short Circuit |
| Dimmable Fluorescent Light System | Select DALI/PWM Dimmable LED | Dimmer Function Failure |
Difference Between Incandescent And LED Lights
Incandescent lights waste so much energy that they’ve been banned in many countries.
Scientifically proven: for every 100W of electricity consumed by an incandescent, only 5W is converted into light energy, while remaining 95W is wasted as infrared heat radiation. However, led can output same luminous flux (5000lm) at 50W of power consumption, while generating only 1/10 heat of an incandescent.

| Scenario | LED Solution | Incandescent Feasibility |
|---|---|---|
| Supermarket Fresh Food Area | 5000K High CRI LED (CRI>90) | ❌ Infrared heat radiation accelerates food spoilage |
| Factory Warehouse | 200W LED High Bay Light | ❌ 500W incandescent light, doubles electricity bill |
| Outdoor Advertising | IP67 Waterproof LED Module | ❌ Burst rate increases by 300% in rainy and foggy weather |
Fluorescent Light vs Incandescent Light
Incandescent lights have low luminous efficacy (8-15 lm/W) and lifespan of less than 2,000 hours. They generate light by heating the filament, light temperatures reaching as high as 260°C. However, they have a high color rendering index (CRI) of 90-100.
Fluorescent lights have a high luminous efficacy (40-70lm/W) and a lifespan of less than 15,000 hours. They start up more slowly but produce more light with less energy consumption and generate almost no heat.
Expanded Applications of LED Lighting
Residential Lighting
LED lights is increasingly replacing incandescent bulbs in homes due to its efficiency and versatility. From warm-toned lights for cozy living spaces to bright, cool lights for kitchens, LED lights cater to every need.
Industrial and Commercial Lighting
Industries and businesses favor LED technology for its cost-effectiveness and durability. High bay LED lights are perfect for warehouses, while LED floodlights are ideal for outdoor areas.
People Also Ask
Is it difficult to conversion from fluorescent light to LED?
Converting from fluorescent to LED lighting is generally not a hassle, but the convenience depends on the type of lighting fixture you originally use.
- If you’re just replacing tubes, you can usually just swap it out.
- If you need to replace the entire light, it’s also a good option because you don’t have to worry about it later.
How to convert fluorescent lights to led?
Converting to LEDs isn’t just about installation; it also requires considering lighting quality, such as brightness, color temperature, and illuminance, to ensure the user experience is not compromised after the upgrade.
Steps for Convert Fluorescent Lights to LED:
- Confirm lights parameters: lumen, illuminance, color temperature, color rendering index, and beam angle.
- Light type: Whether you’re replacing tube or the entire light.
- Compatible LED tube or light: Ensure size, voltage, and connector match.
- Whether wiring is required: Some LED tubes require ballast removal or rewiring.
- Install new light: Insert the LED tube or replace the entire light.
- Test lighting: Verify that it’s functioning properly after powering on.
What are applications of fluorescent light vs incandescent light?
Incandescent lights were better for creating atmosphere, while fluorescent lights were used for functional lighting. However, they have now been largely replaced by LEDs, which can meet the needs of both applications.
- Fluorescent lights: Offices, classrooms, shopping malls, hospitals, garages, kitchens, etc.
- Incandescent lights: Residential bedrooms, decorative lighting, chandeliers, etc.








