Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
We often hear the term “beam angle” when it comes to floodlights. But do you really understand beam angle? Why is it so crucial to lighting coverage and uniformity? This article will explain the concept and calculation formula of beam angle in detail.
What is Beam Angle?
Beam angle refers to the width or spread of the beam of light emitted by a lamp. The line along which light emits maximum light intensity is called the optical axis.
- B50% (FWHM, Full Width at Half Maximum)
This is the most commonly used definition of beam angle internationally. The angle between the two directions where the light intensity drops to 50% of the maximum intensity on the plane of the lamp’s optical axis is the beam angle. - B10%
The angle between the two directions on the luminaire’s optical axis where the light intensity drops to 10% of the maximum intensity. Some manufacturers use B10% because this indicates a wider beam angle.
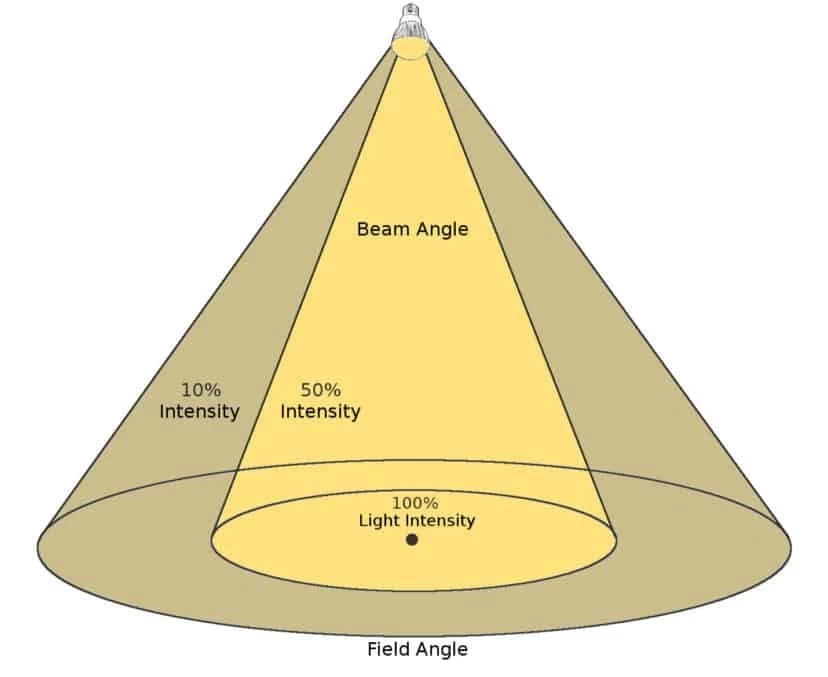
For example: Center light intensity of a luminaire is 10,000 cd.
- Light intensity is maximum at 0° (10,000 cd).
- Light intensity at ±30° is 5,000 cd.
- Light intensity at ±45° is 1,000 cd.
So the beam angles are: B50% beam angle = 60° (because it goes from –30° to +30°); B10% beam angle = 90° (because it goes from –45° to +45°).
| Category | Typical Range (°) | Applications | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Narrow | 10°–30° | Facades, statues, long-distance focus | High intensity, sharp contrast, small area |
| Medium | 30°–60° | Entrances, courtyards, walkways | Balanced coverage and brightness |
| Wide | 60°–120° | Parking lots, warehouses, sports fields | Wide area, even light, lower center lux |
| Note: Ranges are typical values. Beam angle usually defined at B50% (FWHM). | |||
Beam Angle Calculator
The beam angle calculator we use is based on a known beam angle to estimate its irradiation range and installation height. This is because the beam angle is an optical measurement value that is measured by the manufacturer in the laboratory and marked in the product parameters.
Beam angle calculator formula: D = tan (θ / 2) × L
Meaning:
- D = Radius of illumination area
- θ = Beam angle
- L = Mounting height
Example calculation: If lights is installed at height of 5 meters and has a beam angle of 60°:
- D = tan(30°)×5 = 2.89m
The same is true for calculating the installation height when the irradiation range is known. We can directly calculate the result.
Formula: D = L × tan(θ / 2)
How to choose right beam angle?
Lighting Needs
- To highlight sculptures and paintings (accent lighting): Choose a narrow beam (15°-24°).
- To illuminate walls and paintings (wallwash lighting): Choose a medium beam (24°-36°).
- To provide basic spatial lighting or illuminate corridors: Choose a medium-wide beam (36°-45°).
- To illuminate an entire room (ambient lighting): Choose a wide beam (>60°).
- To illuminate large outdoor areas: Choose a floodlight with an extra-wide beam (>90°).
Illumination Distance
The farther the light source is from the object being illuminated, the narrower the beam angle required to produce the same spot size.
| Application | Recommended Beam Angle | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Spotlighting artwork or statues | 10°–30° (Narrow) | Focus light on a small area, create contrast |
| General room or corridor lighting | 30°–60° (Medium) | Balanced coverage and brightness |
| Parking lots, sports fields, warehouses | 60°–120° (Wide) | Illuminate large areas evenly, reduce shadows |
| Accent lighting for shelves or display cases | 20°–40° (Narrow to Medium) | Highlight products without spilling light |
| Outdoor garden or landscape lighting | 30°–90° (Medium to Wide) | Provide soft, even illumination over plants and paths |
| Note: Beam angles are approximate; select based on ceiling height and area size. | ||
Conclusion
Beam angle determines the shape and spread of light. Understanding and using beam angle can provide you with a better lighting experience. When choosing a lamp, it is important to focus on beam angle, not just wattage (brightness) and color temperature (color).
We are a professional manufacturer of LED lighting for industrial and commercial applications. Our fixtures offer a variety of beam angles. Contact us to customize your lighting solution.
People Also Ask
How to measure beam angle?
Beam angle is typically measured by the manufacturer in the laboratory using a photometer or light meter. The standard method is to determine the angle at which the light intensity drops to 50% of its maximum value (B50%), either from IES data or by measuring directly at the surface.
What beam angle is best for floodlights?
The optimal beam angle for a floodlight depends on the specific application:
- Narrow beam angle (10°–30°): Used to highlight specific objects or areas.
- Medium beam angle (30°–60°): Used for general area lighting.
- Wide beam angle (60°–120°): Used for illuminating large spaces such as sports fields and parking lots.
Is the beam angle of a luminaire fixed after leaving the factory?
Yes. Most LED fixtures have a fixed beam angle defined by their optics. Changing it usually requires replacing the lens or reflector. Some specialized adjustable spotlights allow modifying the beam angle, but for typical floodlights, the beam angle is predetermined.








