Table of Contents
Toggle1. Introduction
But how long do LED lights really last? What factors affect their lifespan? How can extend lifespan of lights? This chapter explains the two major areas of home and industrial LED lighting.
2. Theoretical Life Of LED Lights
The theoretical life of LED lights usually refers to the time it takes for the light to decay to 70% of the initial brightness (L70 standard), industrial grade can reach the L90 (light decay 10%) standard, but the actual life is significantly affected by heat dissipation, power quality, and operating environment.
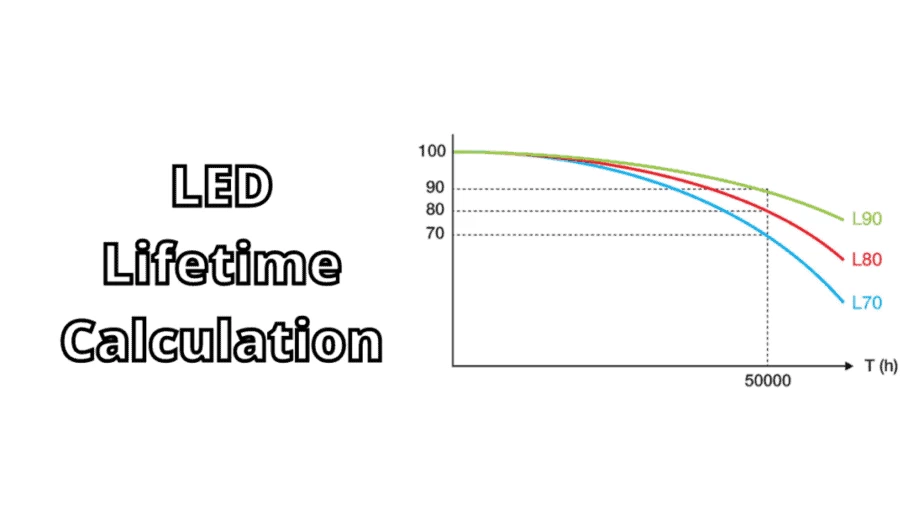
2.1 Specific explanation of light decay and longevity
In fact, the light decay of any LED starts from the first day, that is, the brightness will dim over time, but the speed is very slow in the early stage.
| Standard | Meaning |
|---|---|
| L70 | The time when the luminous flux drops to 70% (commonly used in general lighting) |
| L80 | The time when the luminous flux drops to 80% (commonly used in high-end lighting) |
| L90 | The time it takes for the light to decay to 90%, and the light quality is still very high (used in medical and museums) |
| B50 | 50% of the lamps have a light decay value that reaches the target value (e.g. L70) |
If the nominal life of an LED light is 50,000 hours (L70), it means:
Under normal use and appropriate heat dissipation conditions, its brightness after 50,000 hours is about 70% of the factory brightness. At this time, it can still be used, but the brightness has begun to decrease significantly.
Common Misconceptions : It does not mean that the lamp will completely burn out or not light up after 50,000 hours. It also does not mean that the light will start to decay after 50,000 hours.
2.2 Theoretical LED Light Longevity Industry Standard
| Type | Theoretical Life (Hours) | Continuous Use Years | Recommended Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home LED | 15,000 – 25,000 hours | 5 – 8 years(8 hours per day) | bedroom, kitchen, living room |
| Industrial LED | 50,000 – 100,000 hours | 14 – 28 years(10 hours per day) | factories, warehouses, tunnels, ports, stadiums, parking lots, etc. |
2.3 Why Industrial LEDs Last Longer?
| Lifespan Factor | Residential LED | Industrial LED |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Dissipation Design | Basic aluminum or plastic casing, passive cooling | Die-cast aluminum + fin structure / active fan cooling, high thermal conductivity |
| Driver Quality | Basic constant current driver, 80%~85% efficiency | Wide voltage industrial-grade driver (100–277V), >90% efficiency, surge protection |
| LED Chip Quality | Mid-tier chips (e.g. 2835/3030) | High-efficiency COB or flip-chip (e.g. Lumileds, CREE) |
| Protection Rating | IP20 ~ IP40 (dust protection only) | IP65/IP66 (waterproof and dustproof), vibration & corrosion resistant |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C – +40°C | -50°C – +75°C, suitable for harsh environments |

3. How Is LED Last Long Calculated?
The longevity of LED is not calculated by simple mathematical formula, but is based on the comprehensive results of accelerated aging experiments + mathematical model deduction. The core goal is to predict the degree of light decay (such as L70/L80/L90 standards).
3.1 LM-80 Test (luminous decay experiment of lights)
Test object: Only for LED chips/light modules (excluding power driver)
Conditions: Under constant current drive, place the LED in three temperature environments: 55℃/85℃/105℃.Continuously light up for 6,000 hours (about 250 days), and measure the luminous flux every 1,000 hours
Output: Generate a light decay curve (temperature vs. brightness decay rate)
3.2 Why is actual lifespan much lower than theoretical?
- Power supply short board effect
The life of the driving power supply is usually only 10,000 to 30,000 hours (electrolytic capacitors dry up, MOS tubes burn out), while the theoretical life of the lamp beads exceeds 50,000 hours. - Industry consensus: The life of the whole light = min(light bead life, power supply life)
- Heat dissipation design defects
Poor quality heat sinks cause the junction temperature (Tj) to soar: for example, in a nominal 25℃ environment, the actual Tj can reach 120℃ (far exceeding the chip temperature resistance of 85℃). - Nonlinear deterioration of the light decay curve
The initial light decay is slow (<3% in the first 2,000 hours), and it accelerates in the later stage (such as annual decay >10% after 50,000 hours).
3.3 Industry Truth:
LED street lights claiming to have a “100,000-hour lifespan” are actually tendered for municipal projects based on an L80 lifespan of ≥60,000 hours (approximately 7 years).
The lifespan of household LED lights is marked as 25,000 hours, but due to reduced power supply, the actual average failure time is 8,000~15,000 hours (data source: CNAS laboratory sampling).
In actual use, power supply and heat dissipation are the main factors affecting the lifespan. When purchasing, you should pay close attention to the heat dissipation design and power quality, and don’t be superstitious about the “100,000 hours” propaganda.
4. Extend Actual Life of LED Lights
How long do LED lights last is not only related to product quality, but also closely related to usage habits, installation methods, usage environment, etc. So how should we choose long-life LED lights and what are the details of daily use?

4.1 Industrial LED Life Extension Solution
Heat dissipation is extremely important, and the material of LED lamps should be made of aluminum alloy. Because in industrial lighting, there will not only be a changing environment, but also long-term operation. It should have a unique heat sink and structure, die-cast aluminum greater than 4mm, and copper heat pipes.
- Be sure to choose the right lamp for the right place, for example, ordinary high-bay lamps cannot be used in high-temperature workshops.
- Avoid dense installation (spacing > 1.5 times the width of the lamp body), and reserve air ducts in high-temperature environments. Clean the heat sink fins regularly (once a quarter, once a month in dusty environments).
- Choose a power supply with wide voltage input (90-305V AC), efficiency > 92%, and standard TVS surge protection (anti-20kV pulse).
- Automatically reduce power to 50% during midnight (such as Philips CityTouch system), which can extend life by 2.3 times.
- With high protection level IP66/IP68, dustproof, waterproof, corrosion-resistant and vibration-proof
4.2 Home LED Life Extension Solution
Choose hollow design lamps to avoid sealing. There should be good heat dissipation space, and insulation cotton should not be covered. Add a slow start module in high-frequency switching scenes (such as bathrooms) to eliminate cold start current shock. Use a dry soft brush to clean the dust in the gap of the lamp body every six months (water washing will cause power short circuit). If the light flickers or the brightness drops by more than 30%, replace it immediately.
5. Summary of Long Do LED Lights Last
Under normal use, industrial LED lights can last for more than 50,000 hours, and household LED lights can last for more than 20,000 hours. However, this does not mean that they cannot be used after this time. It just means that the brightness will decrease. You can still use them. However, due to multiple factors such as the use environment, heat dissipation, and maintenance, there will be a large deviation. We should adapt to LED lighting correctly and reasonably.
6. People Also Ask
Do LED lights get dim over time?
Yes, strictly speaking, it starts to get darker from the first day, but it is very small in the early stage and you can’t notice it. As the use time gets longer, the degree of darkening will gradually increase, and generally you will feel it after 20,000-50,000 hours.
What shortens the lifespan of LED lights?
Heat accumulation will significantly affect the use time of LEDs, so lights need to have excellent heat dissipation capabilities. Failure to clean accumulated dust and maintain lights will also affect their lifespan.
Can I trust those 100,000 hour LED lights?
The 100,000-hour lifespan marked by the manufacturer is under ideal operating conditions. For example, if our Diamond Ⅰ Plus 75℃ high temperature light is operated only in a 50℃ environment, its lifespan can exceed 100,000 hours. However, if it is only operated in a 75℃ space, the standard lifespan is 50,000 hours. Therefore, you need to judge the lifespan based on the space you use and the light you choose.








