Table of Contents
ToggleVisible Light Definition
Visible light is a type of electromagnetic waves that is visible to human eye. The wavelengths of visible light range from 380 to 750 nm, electromagnetic spectrum is distributed continuously, but only wavelengths within this range can be seen by human eye. And each wavelength corresponds to a specific color.
- Facts about visible light tell us that it’s responsible for colors we see, and without it, we wouldn’t be able to perceive objects.
- What is visible light? It is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that humans can detect. It is sandwiched between ultraviolet light and infrared light.
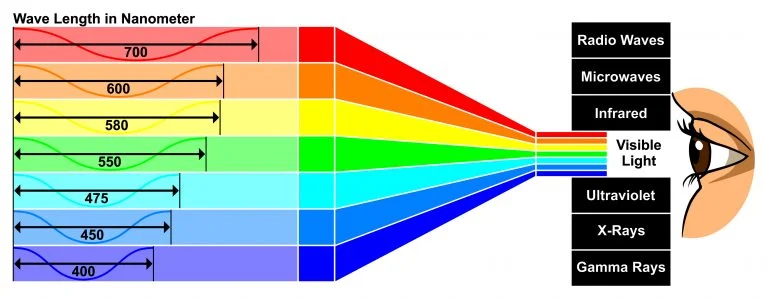
Visible Light Wavelength
The wavelength range of visible light is 380-750nm (some say 400-700nm). It is located between ultraviolet light and infrared light in electromagnetic spectrum, corresponding to various colors of light we see in our lives.
- Light with wavelength shorter than 380 nm is ultraviolet light, which is invisible to human eye;
- Light with wavelength longer than 750 nm is infrared light, which is also invisible.
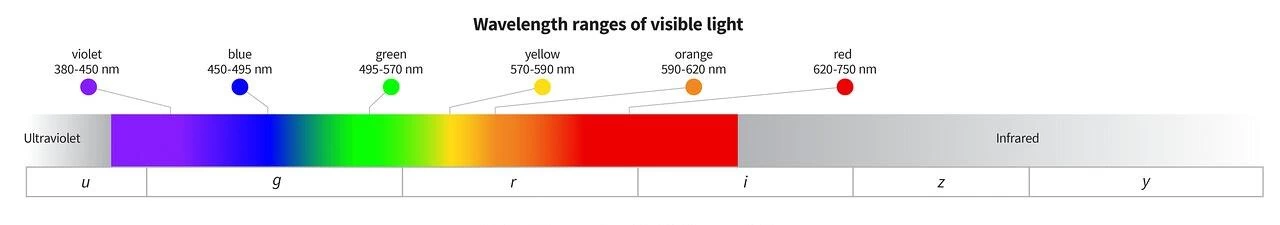
Among visible light, red has the longest wavelength and violet has the shortest wavelength. Visible light range example table:
| Color | Visible Light Wavelength Range (nm) | Central Wavelength | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Violet | 380 – 435 | 415 | Shortest wavelength, high energy, near ultraviolet |
| Blue | 435 – 485 | 470 | Cool color, common in sky and ocean |
| Cyan | 485 – 500 | 492 | Blue-green transition color, ocean color |
| Green | 500 – 565 | 535 | One of the most sensitive wavelengths for human eyes |
| Yellow | 565 – 590 | 577 | Bright and warm, typical of sunlight |
| Orange | 590 – 625 | 610 | Between yellow and red, warm tone |
| Red | 625 – 750 | 680 | Longest wavelength, lower energy, near infrared |
Controversy surrounding the visible light wavelength range:
Some people can perceive light at 310 nm (near ultraviolet) or 1050 nm (near infrared). But, standard visible light range is based on the population average.
Note: Shorter the wavelength, higher the energy of photon. So violet light has highest energy and red light has the lowest.
Visible Light Spectrum Facts
The visible light spectrum is the portion of electromagnetic spectrum visible to the human eye. It spans a continuous wavelength range from 380 to 750 nm. Rather than being divided into distinct colors, it forms a continuous gradient.
The visible light spectrum is a gradient of colors from red to violet, with no fixed color boundaries. Light in 500–600 nm range (especially green) is most sensitive to visual perception.
What makes the “visible spectrum” of light visible to the human eye? It’s all about how light waves interact with the photoreceptors in our eyes:
| Photoreceptor Type | Peak Sensitivity (nm) | Main Function | Light Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cones | ~420–560 | Color recognition (photopic vision) | Bright light (Photopic) |
| Rods | ~500 | Brightness detection (no color) | Low light (Scotopic) |
Applications
- Lighting: LEDs, fluorescent lamps, and incandescent lamps all produce light in various ways across the visible spectrum.
- Displays and Imaging: Display screens mix the three primary colors of red, green, and blue to produce a variety of colors within the visible spectrum.
- Spectral Analysis: Spectrophotometers use visible light to analyze the absorption and transmission properties of substances.
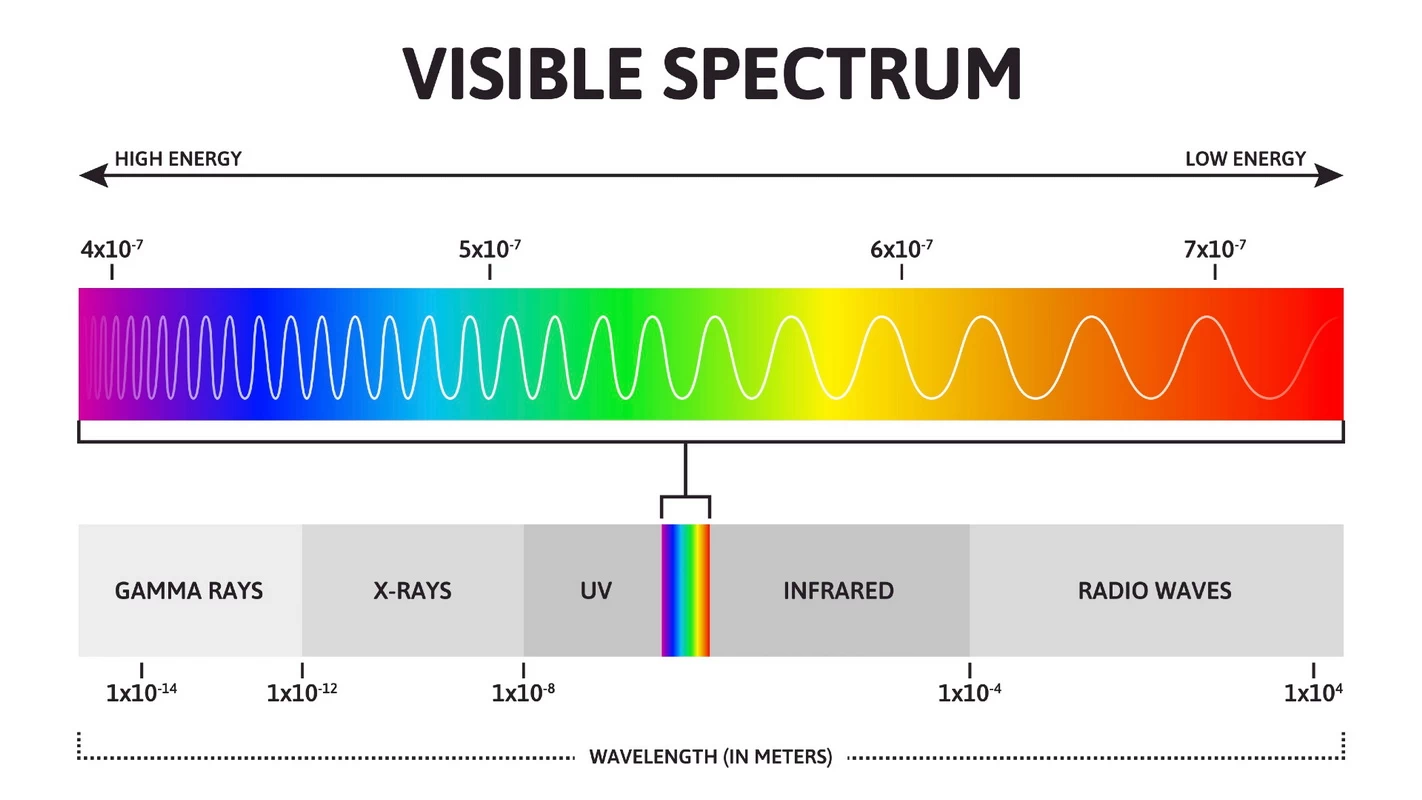
What are the uses of visible light?
- Most common use of visible light is in lighting industry, including home, commercial and industrial lighting. For example, incandescent , fluorescent , and modern LED lights. You can find more information about application of visible light in LED lights.
- Screens and photography: The three primary colors of red, green, and blue can be mixed to produce any color and are used in televisions, computers, and mobile phones.Cameras, projectors, microscopes, and other devices rely on visible light to form images.
- Biology: Blue light can regulate melatonin secretion and help control sleep. Violet-blue light can be used to treat acne. Red light can promote wound healing.
- Photosynthesis: Plants use visible light (440nm blue light and 670nm red light) to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and organic matter.
| Application Area | Visible Light Used | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Lighting | Illumination for daily life and work | LED, fluorescent, Incandescent, street lights |
| Information Technology | Display of images | TV screens, smartphones |
| Medical | Diagnosis, therapy, and biological observation | Phototherapy, surgical lighting, microscopes |
| Industrial & Quality Control | Inspection, color matching, process monitoring | Product inspection lines, colorimeters, optical sensors |
| Arts & Entertainment | Visual effects and color rendering | Stage lighting, photography, cinema |
| Safety & Signaling | Alerting and guiding people | Traffic lights, warning lights, exit signs |
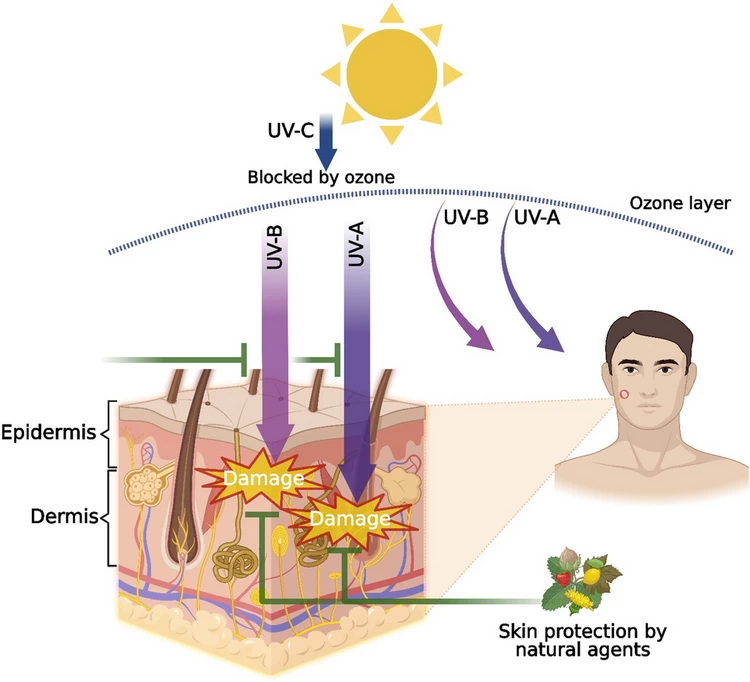
Ultraviolet(UV) and Infrared(IR)
Ultraviolet (wavelength 100-400nm) and infrared (wavelength 750nm-1mm) are not considered visible light and are not included in the visible light spectrum. Their energy and practical applications are very different.
Ultraviolet light (UVA:315–400 nm, UVB:280–315 nm, UVC:100–280 nm)
Ultraviolet light has high photon energy (3.1–124 eV), can break chemical bonds, and can cause sunburn. It is commonly used for disinfection, chemical reactions, and fluorescence detection.
Infrared light
Its wavelength is longer than visible light, but its photon energy is lower, resulting in thermal radiation. It is primarily used for thermal imaging, night vision devices, remote control, and communications.
| Type | Wavelength Range | Key Features & Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Ultraviolet (UV) | 10–400 nm | High energy; causes chemical reactions; used in sterilization UV therapy, fluorescence detection, industrial photochemistry |
| Infrared (IR) | >750 nm Near IR: 0.75–1.5 μm, Mid IR: 1.5–5 μm, Far IR: 5–1000 μm | Lower energy; heat radiation; used in thermal imaging night vision, remote sensing, IR communication, industrial heating |
Although ultraviolet and infrared rays are invisible, they play an irreplaceable role in technology, medicine, and the environment.
Summarize
Visible light refers to the range of wavelengths that can be seen by the human eye. The colors of the visible light spectrum are continuous from red to violet, and they are widely used in our lives.
People Also Ask
What do visible light waves show us?
They help us see objects by reflecting off surfaces and entering our eyes, where they are processed by photoreceptors.
Which color of visible light has the shortest wavelength?
In the visible spectrum, violet light has the shortest wavelengths, ranging from approximately 380–450 nm.
Which color of visible light has the longest wavelength?
In the visible spectrum, red light has the longest wavelength, approximately in the 620–750 nm range.
What colors are in the visible light spectrum?
The visible spectrum is artificially divided into “purple, blue, cyan, green, yellow, orange, and red.”
Strictly speaking, the spectrum’s colors are continuous, without boundaries, and therefore should contain an infinite number of colors.
What are some examples of applications of visible light in the lighting industry?
- White light: Shopping mall lighting, industrial lighting, sports lighting, home lighting, street lighting
- Warm yellow/orange light: Living rooms, dining rooms, and hotels
- Red light: Traffic lights, stage lighting, and outdoor lighting at night
- Green light: Traffic lights, indoor plant areas, hospitals, and meditation spaces
- RGB light: Stage lighting, architectural decorations, and LED light strips








