Índice
ToggleIntroducción
La tecnología de iluminación LED se ha convertido en una fuerza revolucionaria en las soluciones de iluminación modernas. Las luces LED (diodo emisor de luz), que ofrecen un importante ahorro de energía, una luminosidad superior y una vida útil más larga que los métodos de iluminación tradicionales, han ganado una gran popularidad en hogares, industrias y entornos exteriores. Pero, ¿cómo se fabrican las luces LED y qué materiales intervienen en el proceso de producción?

¿De qué están hechas las luces LED?
Los materiales de los LED incluyen chips LED, fósforos, sustratos, radiadores, placas de circuitos, componentes electrónicos, carcasas, reflectores y lentes.
Fuente de luz
La fuente de luz de un LED es el chip LED, responsable de producir la luz. El chip se coloca sobre un sustrato y se encapsula con un recubrimiento de fósforo (en el caso de los LED blancos) para modificar color de la luz emitida.
Accionamiento y control
El controlador LED es un componente esencial que regula la corriente eléctrica y garantiza que se suministre la cantidad correcta de energía al chip LED. Convierte la CA (corriente alterna) de una fuente de alimentación en CC (corriente continua), que es lo que necesitan los LED para funcionar.
Disipación del calor
Un calor excesivo puede degradar el rendimiento de los chips LED y reducir su vida útil. Los disipadores de calor, normalmente de aluminio, se utilizan en las luces LED para alejar el calor del chip LED y dispersarlo de forma segura. También hay grasa térmica para rellenar el hueco entre el chip y el radiador y mejorar la eficacia de la conducción del calor.
Estructura y óptica
En las luces LED se suelen utilizar lentes/reflectores para controlar la distribución de la luz, enfocándola o difuminándola en función de la aplicación. Las lentes suelen estar hechas de materiales duraderos, como vidrio o plástico, y están diseñadas para mejorar el rendimiento y la eficiencia del LED dirigiendo la luz hacia donde se necesita.
La carcasa de las luces LED, de aluminio fundido a presión o plástico, integra todos los componentes y protege la luz.
Material de iluminación LED mesa completa:
| Componente | Función | Materiales comunes / Notas |
|---|---|---|
| Chip LED (Emisor) | Convierte la energía eléctrica en luz | Materiales semiconductores GaN / InGaN / GaAs |
| Fósforo | Convierte la luz LED azul/UV a blanco u otras temperaturas de color | YAG:Ce, fósforos a base de silicato; aplicados como recubrimiento |
| Sustrato / PCB | Soporte mecánico y recorrido térmico para los chips | PCB de aluminio, PCB de cobre, sustratos cerámicos |
| Disipador de calor / Gestión térmica | Disipa el calor para mantener el rendimiento y la vida útil | Extrusión/troquelado de aluminio, cobre, materiales de interfaz térmica |
| Controlador / Fuente de alimentación | Convierte la red eléctrica en corriente/tensión constante para los LED | Circuitos integrados, condensadores, inductores; encerrados en carcasas de plástico o metal |
| Lente / Óptica | Controla la distribución de la luz y el ángulo del haz | PMMA (acrílico), PC (policarbonato), vidrio |
| Reflector / Óptica secundaria | Mejora la uniformidad de la luz y dirige el flujo luminoso | Plásticos revestidos de aluminio, aluminio anodizado |
| Carcasa / Recinto | Protege las piezas internas y facilita el montaje | Aluminio, acero, plásticos PC/ABS; acabado con recubrimiento en polvo o anodizado |
| Juntas y empaquetaduras | Proporciona protección contra la penetración y resistencia a las vibraciones | Silicona, caucho EPDM, encapsulado de poliuretano |
| Conectores y cableado | Conexión eléctrica entre el driver, el LED y la red eléctrica | Hilos de cobre, bloques de terminales, uniones soldadas, mazos de cables |
¿Cómo se fabrican los LED?
El proceso de fabricación de los LED implica múltiples pasos, desde la preparación de las obleas semiconductoras hasta el montaje final del producto de iluminación. He aquí un resumen de cómo se fabrican las luces LED.
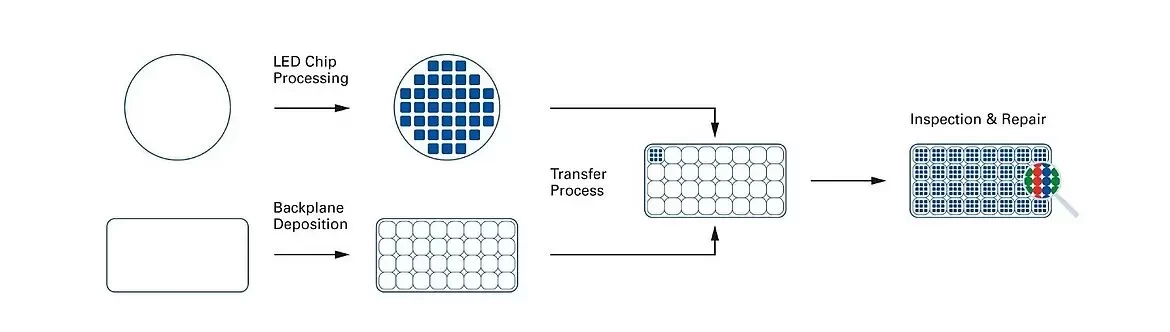
- Preparación de material semiconductor
El primer paso en la fabricación de LED es la preparación del material semiconductor, normalmente nitruro de galio (GaN) o arseniuro de galio (GaAs). Estos materiales se utilizan para crear las obleas semiconductoras, que se cortan en finas capas. - Fabricación de chips LED
A continuación, las obleas semiconductoras se procesan para crear chips LED. El proceso implica:
Dopado: Introducción de impurezas en el material semiconductor para crear regiones tipo p y tipo n, esenciales para la función del diodo.
Grabado: Creación de la superficie emisora de luz del chip LED. - Revestimiento de fósforo
En el caso de los LED blancos, se aplica un recubrimiento de fósforo al chip LED. El fósforo convierte la luz azul o ultravioleta emitida por el chip LED en un amplio espectro de luz visible, normalmente blanca. - Montaje de componentes
El chip LED se monta en un sustrato y se conecta al driver, el disipador de calor y otros componentes esenciales. A continuación se añade la lente para controlar la distribución de la luz emitida. - Pruebas y control de calidad
Tras el montaje, se comprueba el rendimiento de cada LED, incluidos el brillo, la precisión del color y la eficiencia energética. Las estrictas medidas de control de calidad garantizan que el producto final cumpla las normas necesarias.
¿Cuál es el proceso de fabricación de LED?
I+D y diseño
El proceso comienza con la investigación y el desarrollo (I+D), donde los ingenieros diseñan nuevos productos LED y optimizan los diseños existentes para mejorar su rendimiento. Las innovaciones pueden incluir avances en materiales semiconductores, diseños de chips LED y técnicas de disipación del calor.
Investigación de laboratorio
En el laboratorio, los científicos realizan análisis de materiales y pruebas de rendimiento de los chips de LED para optimizar la eficiencia luminosa y garantizar la máxima calidad de la emisión de luz. El objetivo es aumentar la fiabilidad de las obleas semiconductoras y la longevidad del producto LED final.
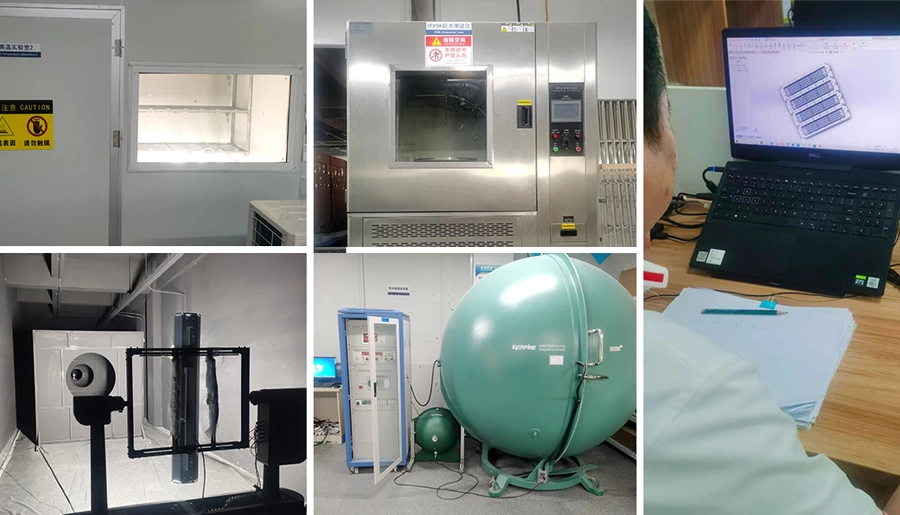

Fabricación de herramientas y maquinaria
En esta fase se desarrolla la maquinaria de utillaje que se utilizará en el proceso de producción de los LED. Se diseñan máquinas especializadas para fabricar las obleas semiconductoras y otros componentes necesarios para ensamblar los LED.

Máquina de moldeo de poliéster y equipos de espumado
Las máquinas de moldeo de poliéster se utilizan para encapsular los chips LED en un material protector que les proporciona resistencia a la humedad y los protege de los factores ambientales. Este paso es esencial para garantizar la durabilidad y fiabilidad del producto final.
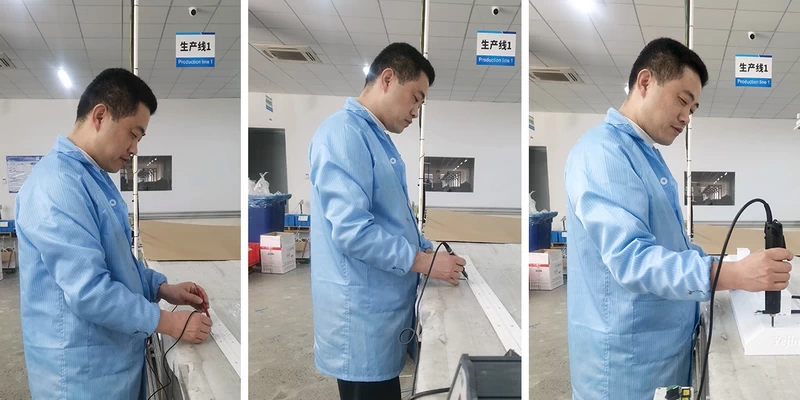
Montaje de componentes
Los chips LED se ensamblan cuidadosamente con otros componentes, como el disipador de calor, el controlador y la lente. Este proceso garantiza que las luces LED funcionen correctamente y estén listas para su uso en diversas aplicaciones.

Pruebas y control de calidad
Tras el montaje, cada luz LED se somete a rigurosas pruebas para garantizar que cumple las normas de rendimiento y seguridad. Esto incluye pruebas de:
- Eficacia luminosa
- Rendimiento eléctrico
- Disipación del calor
- Impermeabilidad y resistencia medioambiental
Resumen
La tecnología de iluminación LED representa un importante salto adelante en las soluciones de iluminación energéticamente eficientes. Al entender de qué está hecha la iluminación LED y el flujo del proceso de fabricación de LED, queda claro que la producción de luces LED implica tecnología punta, ingeniería de precisión y materiales avanzados como los semiconductores.
Ledrhythm dispone de un completo sistema de fabricación de iluminación LED. Vea nuestro control de calidad y información de la empresa. No dude en Contacto para personalizar su solución de iluminación LED.
La gente también pregunta
¿Cómo produce luz un led?
El principio de la emisión de luz de los LED es que, cuando la corriente pasa por una unión PN de material semiconductor, los electrones y los huecos se recombinan en la zona de unión y liberan energía. Esta energía se emite en forma de fotones, generando así luz visible o luz en otras bandas.
- Semiconductor PN: la estructura fundamental de la luminiscencia.
- Recombinación electrón-hueco: Proceso físico por el que se produce la luminiscencia.
- Energía liberada en forma de fotones: Energía convertida en luz durante la recombinación.
- Electroluminiscencia: Conversión directa de energía eléctrica en luz.
¿Con qué materiales se fabrican las luces LED?
Las luces LED se componen principalmente de chips LED, materiales de embalaje, circuitos de accionamiento, disipadores de calor, lentes y carcasas.
¿Es complicado el proceso de fabricación de los LED?
Sí. El proceso de fabricación de LED es realmente complejo y técnicamente difícil, ya que implica diversos procesos de precisión, como la física de los semiconductores, la ciencia de los materiales, la termodinámica y la ingeniería óptica.











