Cómo funciona la regulación LED: iluminación exterior e interior
Regulación LED es un aspecto crítico de los sistemas de iluminación modernos, especialmente en entornos industriales como fábricas, puertosy estadiosdonde las necesidades de iluminación pueden variar considerablemente. Comprender cómo Luces LED regulables y las diferentes tecnologías implicadas es clave para optimizar el consumo de energía, mejorar la calidad de la luz y prolongar la vida útil de las luminarias.
¿Qué es la Regulación?
Regulación se refiere al proceso de ajuste de la brillo de las luces LED para satisfacer distintas necesidades de iluminación. Reduciendo o aumentando el flujo luminoso de la fuente de luz, puede adaptar el entorno de iluminación a distintas aplicaciones. La capacidad de luces LED tenues es crucial en entornos como fábricas, almacenes y estadios deportivos, donde los niveles de iluminación deben ajustarse en función de la eficiencia o el ambiente.
Luces LED regulables: Métodos y tecnologías
Atenuación de las luces LED puede lograrse mediante varios métodos. Cada método tiene aplicaciones específicas según el entorno y el control de iluminación deseado. En entornos industriales como puertos o estadios, una iluminación fiable y eficaz sistemas de regulación para luces LED son esenciales tanto para la iluminación interior como para la exterior.
1.Regulación PWM (modulación por ancho de pulsos)
En Método de regulación PWM convierte una señal analógica en digital controlando el ciclo de trabajo de la onda cuadrada, que ajusta la corriente en el circuito. Variando los tiempos de "encendido" y "apagado" de la señal, se puede reducir la cantidad de corriente que llega a la luz, consiguiendo una iluminación suave y eficaz. atenuación.
2.Regulación de tensión
Se trata de ajustar el tensión suministrado a la luz. En Sistemas de iluminación LEDespecialmente en las fuentes de alimentación con inversor de medio puente, la atenuación se consigue controlando la tensión continua. Esto modifica la corriente de la lámpara, lo que reduce la potencia luminosa y produce un efecto de atenuación.
3.Regulación por modulación de frecuencia de impulsos
Este método altera la frecuencia de funcionamiento del balasto. Al aumentar la resistencia del inductor del balasto, se reduce la corriente total. Este método se utiliza a menudo en los sistemas de iluminación fluorescente, pero puede aplicarse a Regulación LED para lograr resultados similares.
4.Regulación por fases
El control de fase es un método muy utilizado para atenuación incandescentes y también puede aplicarse a Luces LED. A tiristor se utiliza para controlar el ángulo de fase de la señal de CA, lo que reduce eficazmente la tensión de salida. Esto permite controlar con precisión el nivel de brillo de la luz.
5.Regulación de corriente constante
En método de regulación de corriente constante consiste en regular la corriente que circula por la luz. Regulando la corriente con un control analógico, se puede controlar eficazmente el brillo de Luces LEDque ayuda a mantener una potencia luminosa constante aunque cambie la luminosidad.
6.Regulación resistiva
En este método, se coloca una resistencia variable en serie con la luz. Al ajustar la resistencia, la corriente disminuye, lo que reduce la luminosidad. Aunque no es el método más eficaz para Regulación LEDEn algunas aplicaciones, es sencillo y eficaz.
7.Regulación escalonada
Este método es sencillo: cambiando el interruptor de encendido en un patrón específico, puedes conseguir varios niveles de brillo. Se suele utilizar en Iluminación LED para espacios comerciales e industriales que no requieren una regulación infinitamente variable.
8.Regulación analógica
En este método, el brillo del LED se ajusta modificando la señal de tensión mediante un control analógico. La regulación analógica es precisa y eficaz, pero a veces puede dar lugar a una salida de luz incoherente en comparación con métodos digitales más modernos como PWM.
Tabla: Comparación de las tecnologías de regulación LED más comunes
|
Método de regulación |
Aplicación |
Ventajas |
Desafíos |
|
Regulación PWM |
Iluminación industrial y exterior |
Control preciso, eficiencia energética |
Puede provocar parpadeos a bajos niveles de atenuación |
|
Regulación por fases |
Aplicaciones de alta potencia (estadios) |
Sencillo y rentable |
No siempre compatible con todos Luces LED |
|
Regulación 0-10V |
Fábricas, puertos |
Regulación suave y fiable |
Requiere cableado especializado |
|
Regulación DALI |
Aplicaciones comerciales e industriales |
Control escalable e inteligente |
Configuración compleja |
Actualmente, las lámparas LED utilizan fuentes de alimentación conmutadas. Pueden regularse utilizando métodos como la regulación por tiristores, PWM, 0-10V (regulación lineal), DAIL y DMX512.
¿Cómo puede un Dimmer LED ¿Trabajar?
Comprender cómo funcionan los reguladores LED es esencial para establecer un sistema de regulación para LED en entornos industriales. Interruptores reguladores LED controlar la cantidad de corriente que fluye hacia la luz, ajustando los niveles de brillo según la entrada establecida. La capacidad de luces LED tenues no sólo crea flexibilidad, sino que también mejora la eficiencia energética, especialmente en entornos con necesidades de iluminación variables, como estadios y almacenes.
¿Todas las luces LED son regulables?
No todos Luces LED son iguales cuando se trata de atenuación. La pregunta, "¿son regulables todas las luces LED?..." es una pregunta habitual cuando se plantean mejoras de iluminación en entornos comerciales o industriales. La respuesta depende del Regulador de luz LED y la específica Luminarias LED en uso. Por ejemplo, Ritmo LEDcomo sus productos luces LED de gran altura y luminarias LED estancas al vaporestán diseñados específicamente para aplicaciones regulables tanto en interiores como en exteriores.
Luces LED regulables: Ventajas
-
Ahorro de energía: Al reducir el brillo de Luces LEDpuede conseguir importantes ahorros de energía, especialmente en grandes entornos industriales como puertos y fábricas.
-
Vida útil prolongada: Regulación reduce la presión sobre Controladores LEDprolongando la vida útil de las instalaciones.
-
Personalización: Luces LED regulables ofrecen un mayor control sobre el entorno de iluminación, ya sea en estadios, fábricaso edificios comerciales.
Iluminación LED regulable en aplicaciones industriales y comerciales
La capacidad de iluminación LED tenue tiene un profundo impacto en el consumo de energía y la eficiencia operativa, especialmente en entornos industriales y comerciales como fábricas, puertosy estadios. Implantación de una sistema de regulación para LED puede reducir significativamente los costes energéticos manteniendo unas condiciones óptimas de iluminación.
1. Iluminación LED de gran altura
En entornos industriales como almacenes y fábricas, Iluminación LED de gran altura Las luminarias deben ser regulables para adaptarse a las distintas tareas y actividades. Luces LED de gran altura de LED Rhythm están diseñados para funcionar con una amplia gama de atenuadoresque ofrece flexibilidad en espacios amplios.
2. Iluminación LED de baja altura
Para zonas que requieren niveles de luz más bajos, como trasteros o garajes comerciales, luces LED de baja altura y Luminarias LED de baja altura ofrecen la solución regulable ideal. Estas luminarias proporcionan una cobertura uniforme y pueden regularse en función de las necesidades específicas del entorno.
3. Proyectores e iluminación exterior
Iluminación LED exteriorespecialmente en estadios y puertostambién puede beneficiarse de atenuación capacidades. Proyectores regulables permiten ajustar los niveles de luz durante diferentes eventos u horas del día, garantizando el uso más eficiente de la energía.
Problemas comunes con Luces LED regulables
En Regulación LED ofrece numerosas ventajas, es esencial comprender los problemas habituales que pueden surgir:
-
Parpadeo: Mala calidad Reguladores LED o sistemas incompatibles pueden hacer que las luces parpadeen cuando se atenúan.
-
Zumbido: Algunos Luces LED puede producir un zumbido cuando se utiliza con incompatibles interruptores de regulación.
-
Límites de atenuación: No todos Luces LED pueden regularse a niveles extremadamente bajos sin problemas. Comprender los límites de su Sistema de regulación LED es crucial.
Desde la perspectiva de las aplicaciones de regulación: control por cable y control inalámbrico
El control de atenuación por cable tiene una señal estable y fiable. El control de atenuación inalámbrico es fácil de instalar, pero sufre interferencias con facilidad y tiene poca estabilidad.
Método de regulación por cable.
![]()
Método de control de regulación inalámbrico. Los protocolos de transmisión de señales más comunes son Zigbee, Bluetooth y WiFi.

Productos de regulación de Ledrhythm
Ritmo LED ofrece una gama de soluciones de iluminación regulable para aplicaciones industriales y comerciales, entre las que se incluyen:
-
LED Rhythm High Bay LED
-
LED Rhythm Vapor Tight LED
-
Tiras de LED regulables LED Rhythm
Entre los productos de Ledrhythm, farolas, proyectores, lámparas para minería, lámparas trifásicas, etc., todos cuentan con soluciones de regulación. Haga clic aquí para más detalles
Las farolas Ledrhythm, las lámparas industriales y mineras, etc. utilizan sensores de microondas y sensores de luz para lograr el control de la atenuación. El efecto de regulación se muestra en la figura.
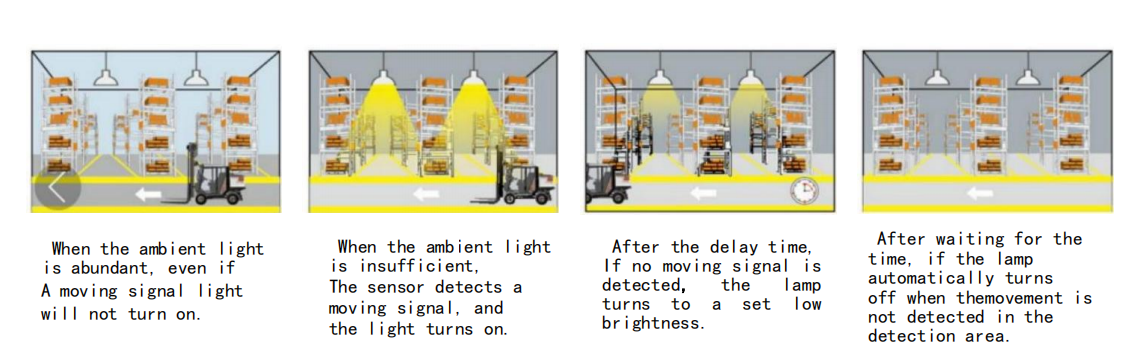
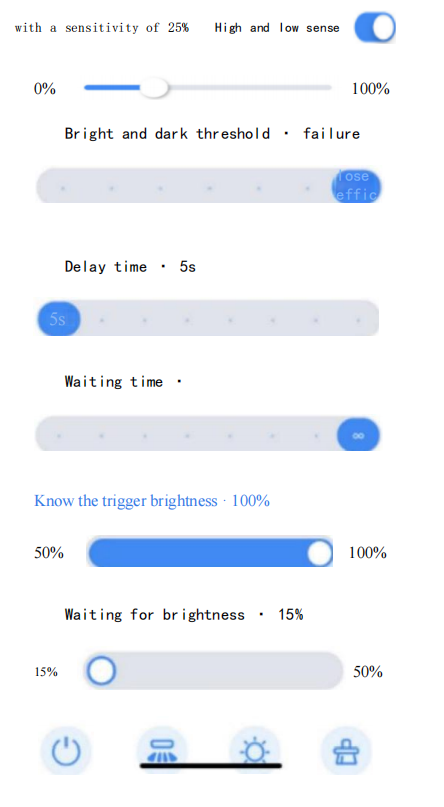
Puede controlar las farolas, los proyectores y las lámparas mineras mediante dispositivos centralizados con cable o control inalámbrico a través de una app. Esto permite ajustar el tiempo de atenuación, el efecto y la agrupación de las luces.
Conclusiones: El futuro de Luces LED regulables en aplicaciones industriales
El futuro de Luces LED regulables en sistemas más inteligentes e integrados que puedan controlarse a distancia o mediante sistemas automatizados. En entornos industriales como fábricas, puertosy estadiosla posibilidad de personalizar los niveles de iluminación con sistemas LED regulables es cada vez más vital para mejorar la eficiencia energética y la flexibilidad operativa.
Ritmo LED productos regulables avanzados, como sus bahía alta y estanco al vapor son líderes en soluciones de iluminación personalizables y energéticamente eficientes para aplicaciones industriales a gran escala.

















