목차
토글LED 와트 등가물에 대한 종합 가이드
LED 등가 전력을 이해하면 기존 조명을 교체할 때 적절한 와트 수를 선택하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
LED 등가 차트 :
참고: 다음은 추정치일 뿐이며, 구체적인 결정은 LED 발광 효율을 기준으로 해야 합니다.
| LED 와트 | 백열등 등가물 | 형광등가물 | 할로겐 등가물 | 광속(lm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5W | 40W | 10W | 30W | ~450 lm |
| 9W | 60W | 15W | 50W | ~800 lm |
| 12W | 75W | 20W | 60W | ~1100 lm |
| 15W | 100W | 25W | 80W | ~1600 lm |
LED 전구 와트는 무엇을 의미하나요?
할로겐이나 백열등과 같은 기존 전구에서는 와트가 밝기를 직접적으로 나타냅니다. 하지만 LED의 경우 와트는 에너지 사용량을 측정하고 루멘은 밝기를 정량화합니다.
LED 전구 와트는 전기 요금에 직접적인 영향을 미치지만 반드시 밝기를 반영하는 것은 아니며, 밝기는 루멘(lm)으로 결정됩니다. LED의 발광 효율(lm/W)이 높을수록 같은 와트에서 더 많은 루멘을 생산하여 더 밝은 빛을 발합니다.
LED와 백열전구 전력량 비교: 과학
백열등에서 LED로 전환한 후 에너지 절약은 80% 이상에 달할 수 있습니다. LED는 텅스텐 전구나 백열전구와 동일한 밝기를 제공하면서도 에너지 소비량은 극히 일부에 불과하여 매우 효율적입니다. 예를 들어
- 60W 백열전구는 9W LED에 해당합니다.
- 100W 백열전구는 18W LED에 해당합니다.

LED 전구 와트 및 루멘
LED 기술은 기존 백열전구와 다르기 때문에 LED로 전환하면 전력 소모량에 대한 우려가 제기되는 경우가 많습니다. 동일한 밝기(루멘)를 달성하기 위해 LED 조명은 훨씬 적은 에너지(와트)를 사용합니다.
이 글에서는 필요에 따라 가장 적합한 전구를 선택할 수 있도록 8W, 15W, 40W, 60W, 75W, 100W 등 다양한 LED 전구의 와트 환산값을 세분화하여 설명합니다. 또한 최첨단 기술과 뛰어난 에너지 효율을 결합한 LedRhythm의 조명 제품도 소개합니다.
와트에서 루멘으로의 변환은 모델과 브랜드에 따라 크게 달라지는 발광 효율(lm/W)에 의해 결정됩니다.
예를 들어, 차트 와트를 루멘으로 환산하면 80-120 lm/W입니다.
| LED 전력(W) | 광속 범위(lm) | 등가 백열전구 전력(대략) |
|---|---|---|
| 5W | 400 - 600 lm | ≈ 45W - 55W |
| 8W | 640 - 960 lm | ≈ 65W - 85W |
| 10W | 800 - 1200 lm | ≈ 80W - 100W |
| 15W | 1200 - 1800 lm | ≈ 110W - 150W |
| 20W | 1600 - 2400 lm | ≈ 140W - 180W |
일반적인 전구 유형에 대한 LED 와트 수
8와트 LED 등가물
8W LED 조명은 기존 60W 백열등과 거의 비슷한 밝기입니다. 평균 밝기는 800lm입니다.
15W LED 등가
평균 밝기 1500lm 이상의 15W LED 조명입니다.
따라서 15W LED는 기존 100W 백열등을 완전히 대체할 수 있으며 약 85%의 에너지를 절약할 수 있습니다.
40W LED 등가물
5W-7W LED 전구는 40W 백열전구를 대체하여 동일한 밝기를 제공하면서도 훨씬 적은 에너지를 사용합니다.
액센트 조명이나 작업 조명에 이상적입니다.
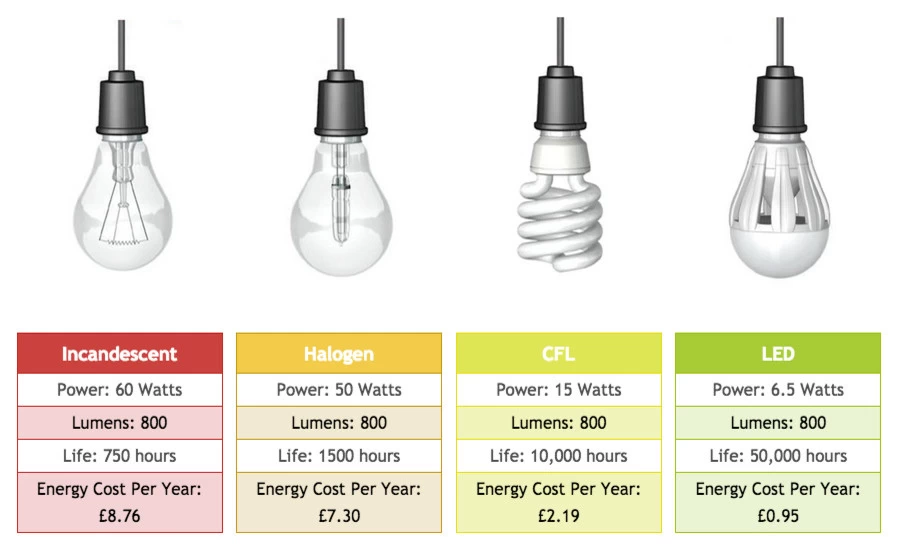
60W LED 비교
9W LED 전구는 800루멘의 밝기를 제공하는 60W 백열전구의 대체품으로 인기가 높습니다.
일반 조명에 적합합니다.
75W LED 등가
13W-15W LED 전구는 1200~1400루멘의 밝기를 제공하므로 75W 백열전구를 대체하기에 적합합니다.
100W에 해당하는 LED 전구
100W 백열등은 약 1600lm입니다. LED 전구의 발광 효율이 80-100lm/W인 경우. 그렇다면 100W 백열등에 해당하는 16W-20W LED 전구.
150W LED 등가
넓은 공간이나 산업용 애플리케이션의 경우 30W+ LED 전구가 150W 백열전구를 대체하여 탁월한 밝기를 제공합니다.
백열등에서 LED 전구로의 전환
와트와 루멘을 이해하면 LED로 전환하는 것은 간단합니다. 다음은 간단한 변환 차트입니다:
| LED 와트 | 백열등 와트 | 루멘 |
|---|---|---|
| 5W-7W | 40W | 400-500 루멘 |
| 9W-10W | 60W | 800-900 루멘 |
| 13W-15W | 75W | 1200-1400 루멘 |
| 18W-20W | 100W | 1600-1800 루멘 |
| 30W+ | 150W | 2400루멘 이상 |
LED와 백열등 및 텅스텐 전구 비교
에너지 효율 및 밝기
LED는 백열전구보다 수명이 25배 더 길고 에너지 소비량은 75% 적습니다.
이에 비해 텅스텐 전구는 빛보다 더 많은 열을 방출하여 효율성이 떨어집니다.
텅스텐 전구 대 LED
- 에너지 효율성
텅스텐 전구: 발광 효율이 매우 낮으며(10-15lm/W), 사용된 에너지 중 95%가 폐열로 변환되고 빛으로 사용되는 것은 5%에 불과합니다.
LED: 발광 효율이 매우 높아(80-150+lm/W) 텅스텐 전구의 1/6~1/10의 에너지만 소비합니다.
LED가 승리합니다: 동일한 밝기에서 85% 이상의 전기료를 절약할 수 있습니다. - 수명
텅스텐 전구: 평균 수명 1,000시간.
LED: 평균 수명 25,000~50,000시간. - 열 및 안전
텅스텐 전구: 표면 온도가 200°C 이상에 달할 수 있어 화상이나 화재의 위험이 있습니다.
LED: 저온(표면 온도 60°C 미만)에서 작동하여 안전성이 크게 향상되었습니다. - 비용
텅스텐 전구: 낮은 단가($1-$5)이지만 전기료와 교체 비용이 매우 높습니다.
LED: 단가가 높지만($3-$20) 장기적으로 90%의 비용 절감 효과를 제공합니다.
LED가 승리합니다: 2년 이내에 투자금을 회수할 수 있어 장기적으로 뛰어난 경제성을 제공합니다.

해당 지역에 적합한 LED 와트 수 선택하기
LED 전구를 선택할 때는 공간의 크기와 용도를 고려하세요:
- 거실: 부드러운 주변 조명을 위해 60W LED 등가물을 사용하세요.
- 주방 및 사무실: 밝은 작업 조명에는 100W LED 등가물을 사용하세요.
- 실외 공간: 투광등이나 보안 조명에는 150W LED에 해당하는 제품을 사용하세요.
LED 전구의 장점: 수명과 효율성
왜 LED 전구를 선택해야 할까요?
- 에너지 절약: LED 전구는 에너지 소비량이 훨씬 적기 때문에 전기 요금이 절감됩니다.
- 긴 수명: LED는 최대 50,000시간까지 사용할 수 있어 교체 주기를 최소화할 수 있습니다.
- 친환경: 에너지 사용량을 줄이면 탄소 배출량이 줄어듭니다.
LedRhythm 조명 제품
LedRhythm은 고품질의 산업용 및 상업용 LED 조명을 제공합니다. 발광 효율 범위는 120~200lm/W이며 전력은 최대 2000W에 달합니다. 그들의 전체 제품 라인 여기를 클릭하세요.
결론
기존 램프와 LED를 비교할 때 가장 중요하게 고려해야 할 사항은 LED의 발광 효율(lm/W)입니다. LED의 발광 효율(80-150+ lm/W)은 백열등(10-15 lm/W)보다 훨씬 높습니다.
결과적으로 저전력 LED(8W)는 고전력 백열등(60W)과 동일한 밝기를 제공하므로 전력 소비를 크게 줄일 수 있습니다. 등가 와트는 전력 소비량이 아닌 밝기의 척도이므로 램프를 선택할 때는 제조업체의 'lm' 등급을 주의 깊게 살펴보세요.
사람들이 자주 묻는 질문
60와트 LED 전구의 등가 와트는 얼마인가요?
60와트 LED 동급 전구는 동일한 밝기를 제공하면서 소비 전력은 8~10와트에 불과합니다.
100와트 백열전구를 LED로 교체할 수 있나요?
예, 100와트 LED 등가물은 약 15~20와트를 소비하며 동일한 밝기를 제공합니다.
저전력 LED 전구도 백열전구만큼 밝나요?
예, 루멘 출력이 높기 때문에 4와트 LED도 40와트 백열전구의 밝기에 맞먹는 효과를 낼 수 있습니다.
LED 광량이 높을수록 좋은가요?
LED 조명은 와트 수가 높다고 해서 반드시 좋은 것이 아니라 적절한 밝기(lm)를 갖춘 것이 가장 좋습니다. 루멘은 조명 공간, 기능 및 밝기 요구 사항에 따라 선택해야 합니다.
조명 공간이 넓고 높은 밝기가 필요한 경우 더 높은 와트의 LED 조명이 더 좋습니다. 그렇지 않으면 눈부심이 심하고 에너지가 낭비됩니다.










