¿Qué factores distinguen a los proyectores LED de los focos? |LEDRHYTHM
En primer lugar, los proyectores LED y los focos son dos luces completamente diferentes. Los proyectores pueden emitir una luz suave y amplia. Tanto si se trata de lámparas para techos altos de fábricas como de lámparas para estadios, pueden proporcionar una iluminación uniforme sin puntos ciegos. La luz de los proyectores es más deslumbrante y puede captar con precisión los puntos clave, como las luces de seguimiento del escenario o los faros de los coches.
¿Qué son los proyectores LED?
Los proyectores tienen un amplio rango de iluminación, luz suave y difusa, y se utilizan principalmente para iluminar grandes áreas. Su ángulo de haz suele estar entre 120°-150°. Los más comunes, como las lámparas de techo, los downlights, las lámparas gran angular, etc., son todos proyectores.
El rango de iluminación de los proyectores es estrecho y la luz está focalizada, por lo que se utilizan para resaltar zonas locales. El ángulo del haz suele estar entre 15° y 45°. Los más comunes, como los focos de seguimiento, las linternas, los faros de coche, etc., son focos.
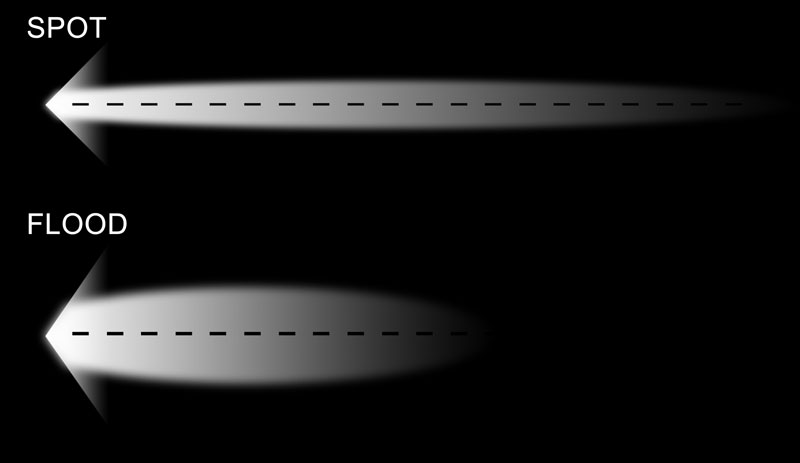
¿Qué distingue a los focos de los proyectores LED?
Diferentes escenarios de uso
Por ejemplo, la iluminación de interiores (habitaciones, salas de conferencias, tiendas, carreteras al aire libre, aparcamientos, luces de estudio) suele utilizar proyectores para proporcionar una iluminación general suave.
La mayoría de los focos de los escenarios, las luces de los escaparates de las tiendas, las luces de los estadios (para iluminar a los jugadores o zonas concretas durante las competiciones deportivas), la iluminación de lugares escénicos, las luces de los coches, las linternas, etc., utilizan focos.
Diferentes ángulos de haz
El ángulo del haz de los proyectores suele estar entre 120° y 150°. El ángulo del haz es grande, por lo que puede iluminar un área mayor y producir una luz suave y difusa.
El ángulo del haz del foco es pequeño, normalmente entre 15°-45°. El pequeño ángulo del haz puede formar un haz enfocado, que producirá una luz relativamente más deslumbrante e intensa.
(fórmula)
Ángulo del haz x 0,018 x distancia de la bombilla = anchura del haz
Por ejemplo, si tiene un proyector de 120 grados a 3 metros de distancia de la luz, la anchura del haz es de 4 metros.
120 grados x 0,018 x 10 pies = 21,6 pies
Si tu foco tiene un ángulo de haz de 40 grados y está a 6 metros de la bombilla, la anchura del haz es de 4,5 metros.
40 grados x 0,018 x 20 pies = 14,4 pies

¿Cómo elegir proyectores y focos LED (proyectores VS focos)?
El requisito previo para elegir proyectores y focos LED es que sean adecuados para su entorno de uso. Usted puede elegir las lámparas que más le convengan a través de los siguientes puntos:
1. Ángulo del haz
El ángulo del haz de los proyectores suele ser de unos 120°, y el de los focos, de unos 15-45°. El ángulo del haz adecuado puede seleccionarse en función del alcance que deba iluminarse.
2. Temperatura de color
La temperatura de color indica el grado de calidez o frialdad de la luz, comúnmente se ven 3000K (blanco cálido), 4000K (blanco neutro), 5000K (blanco luz día), etc. Puede elegir la temperatura de color adecuada según el entorno de uso.
3. Brillo/Lumen
La luminosidad de la lámpara determina el brillo de la luz, y los lúmenes son la unidad de medida de la luminosidad. Para lugares que requieren una luminosidad suficiente, elige lámparas con más lúmenes.
4. CRI
CRI significa índice de reproducción cromática. Cuanto mayor sea el valor, mejor será el efecto de reproducción. Si necesitas mostrar colores reales, elige lámparas con un CRI de 90 o superior.
5. Nivel de impermeabilidad
Elija el nivel de estanqueidad adecuado según el entorno de instalación de la lámpara, normalmente IP20 en interiores e IP65 o superior en exteriores.
6. Calidad y longevidad
Elige productos de marcas conocidas con buenos efectos luminosos y larga vida útil.
Los proyectores LEDRHYTHM tienen un grado de estanqueidad de hasta IP65 y son altamente eficientes y ahorradores de energía. Pueden satisfacer todas las necesidades de los proyectores.








