목차
토글가시광선 정의
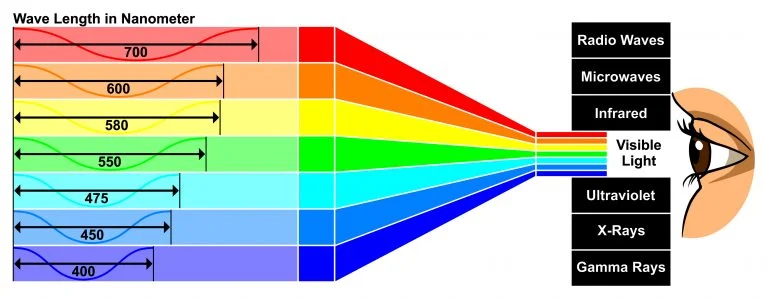
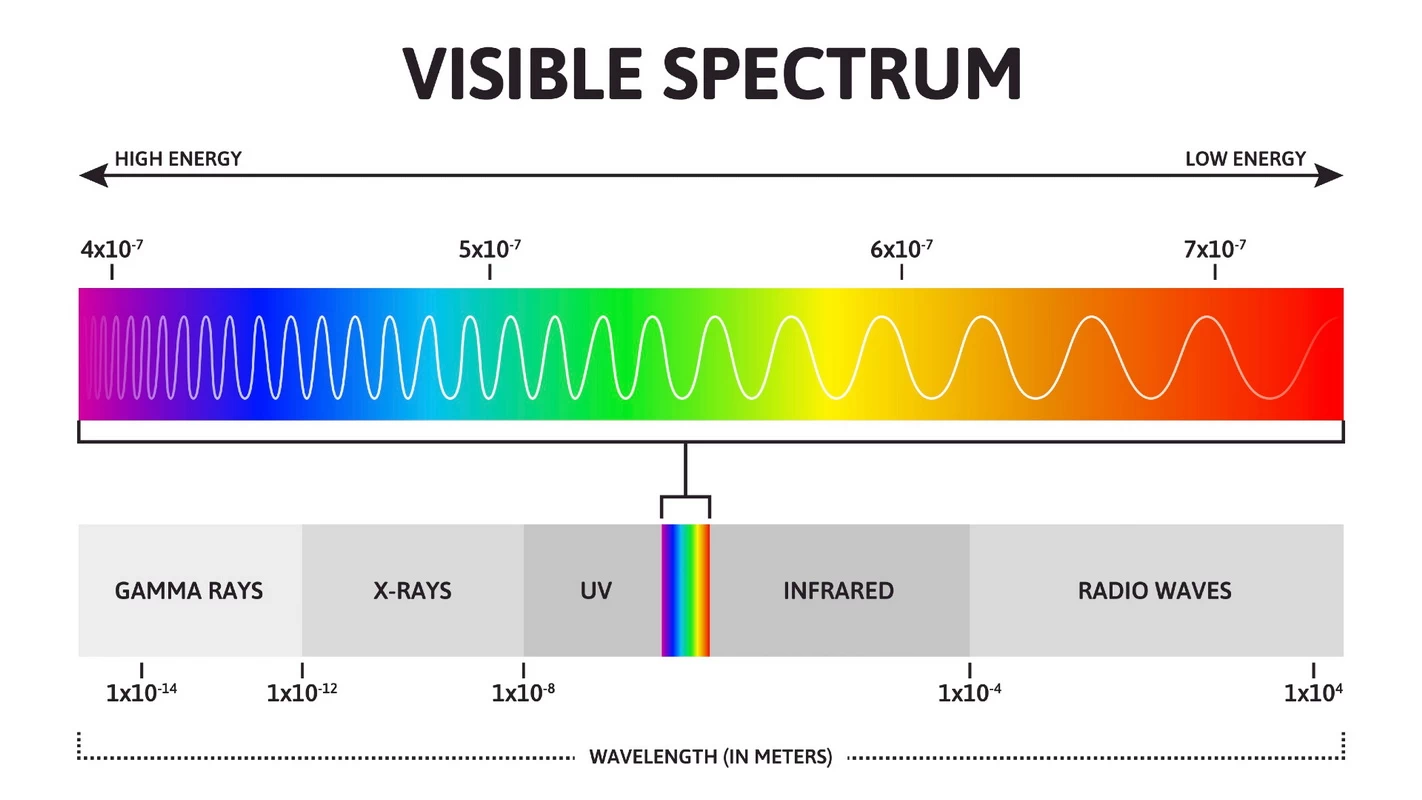
가시광선은 사람의 눈으로 볼 수 있는 전자기파의 일종입니다. 가시광선의 파장은 380~750nm이며, 전자기 스펙트럼은 연속적으로 분포하지만 이 범위 내의 파장만 사람의 눈으로 볼 수 있습니다. 그리고 각 파장은 특정 색상에 해당합니다.
- 가시광선에 관한 사실에 따르면 가시광선은 우리가 보는 색을 담당하며, 가시광선이 없다면 우리는 사물을 인식할 수 없습니다.
- 가시광선이란 무엇인가요? 가시광선은 인간이 감지할 수 있는 전자기 스펙트럼의 일부입니다. 가시광선은 자외선과 적외선 사이에 끼어 있습니다.
가시광선 파장
가시광선의 파장 범위는 380-750nm(일부에서는 400-700nm라고도 함)입니다. 전자기 스펙트럼에서 자외선과 적외선 사이에 위치하며, 우리가 일상에서 보는 다양한 색의 빛에 해당합니다.
- 파장이 380nm보다 짧은 빛은 사람의 눈에는 보이지 않는 자외선입니다;
- 파장이 750nm보다 긴 빛은 적외선으로, 이 역시 눈에 보이지 않습니다.
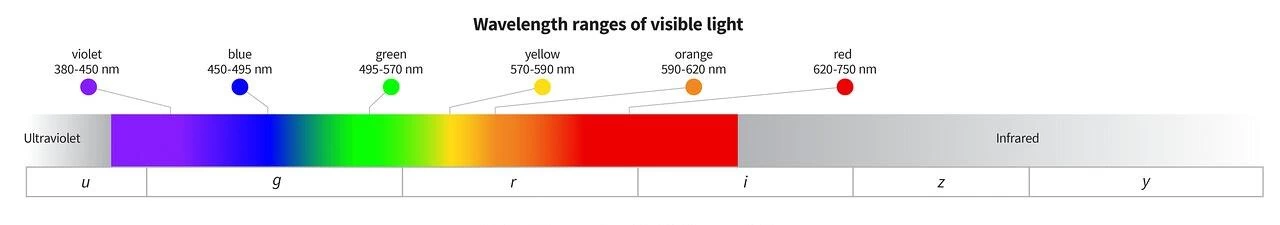
가시광선 중에서 빨간색은 파장이 가장 길고 보라색은 파장이 가장 짧습니다. 가시광선 범위 예시 표입니다:
| 색상 | 가시광선 파장 범위(nm) | 중심 파장 | 특성 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 바이올렛 | 380 - 435 | 415 | 최단 파장, 고에너지, 근자외선 |
| 파란색 | 435 - 485 | 470 | 하늘과 바다에서 흔히 볼 수 있는 시원한 색상 |
| Cyan | 485 - 500 | 492 | 청록색 전환 색상, 바다색 |
| 녹색 | 500 - 565 | 535 | 사람의 눈에 가장 민감한 파장 중 하나 |
| 노란색 | 565 - 590 | 577 | 밝고 따뜻하며 전형적인 햇빛 |
| 오렌지 | 590 - 625 | 610 | 노란색과 빨간색 사이, 따뜻한 톤 |
| 빨간색 | 625 - 750 | 680 | 가장 긴 파장, 낮은 에너지, 근적외선 |
가시광선 파장 범위를 둘러싼 논란:
일부 사람들은 310nm(근자외선) 또는 1050nm(근적외선)에서 빛을 감지할 수 있습니다. 하지만 표준 가시광선 범위는 인구 평균을 기준으로 합니다.
참고: 파장이 짧을수록 광자의 에너지가 높습니다. 따라서 보라색 빛이 가장 에너지가 높고 빨간색 빛이 가장 낮습니다.
가시광선 스펙트럼 정보
가시광선 스펙트럼은 사람의 눈으로 볼 수 있는 전자기 스펙트럼의 일부입니다. 380~750nm의 연속적인 파장 범위에 걸쳐 있습니다. 뚜렷한 색상으로 나뉘는 것이 아니라 연속적인 그라데이션을 형성합니다.
가시광선 스펙트럼은 빨간색에서 보라색에 이르는 색상의 그라데이션으로, 고정된 색상 경계가 없습니다. 500~600nm 범위의 빛(특히 녹색)은 시각적 지각에 가장 민감합니다.
빛의 "가시 스펙트럼"이 사람의 눈에 보이는 이유는 무엇일까요? 광파가 우리 눈의 광수용체와 상호 작용하는 방식에 관한 모든 것입니다:
| 광수용체 유형 | 피크 감도(nm) | 주요 기능 | 조명 조건 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 콘 | ~420-560 | 색상 인식(포토픽 비전) | 밝은 조명(포토픽) |
| 로드 | ~500 | 밝기 감지(색상 없음) | 저조도(스코픽) |
애플리케이션
- 조명: LED, 형광등, 백열등은 모두 가시광선 스펙트럼에 걸쳐 다양한 방식으로 빛을 발산합니다.
- 디스플레이 및 이미징: 디스플레이 화면은 빨강, 초록, 파랑의 3원색을 혼합하여 가시 스펙트럼 내에서 다양한 색상을 생성합니다.
- 스펙트럼 분석: 분광광도계는 가시광선을 사용하여 물질의 흡수 및 투과 특성을 분석합니다.
가시광선의 용도는 무엇인가요?
- 가시광선은 가정, 상업 및 산업 조명을 포함한 조명 산업에서 가장 일반적으로 사용됩니다. 예를 들어 백열등, 형광등, 최신 LED 조명 등이 있습니다. 다음에 대한 자세한 정보를 확인할 수 있습니다. LED 조명에 가시광선을 적용합니다.
- 화면과 사진: 빨강, 초록, 파랑의 3원색은 혼합하여 어떤 색이든 만들 수 있으며 텔레비전, 컴퓨터, 휴대폰에 사용되며 카메라, 프로젝터, 현미경 및 기타 장치는 가시광선에 의존하여 이미지를 형성합니다.
- 생물학: 블루라이트는 멜라토닌 분비를 조절하고 수면 조절에 도움을 줄 수 있습니다. 보라색-파란색 빛은 여드름 치료에 사용할 수 있습니다. 적색광은 상처 치유를 촉진할 수 있습니다.
- 광합성: 식물은 가시광선(440nm 청색광과 670nm 적색광)을 사용하여 이산화탄소와 물을 산소와 유기물로 전환합니다.
| 적용 분야 | 가시광선 사용 | 예 |
|---|---|---|
| 조명 | 일상과 업무를 위한 조명 | LED, 형광등, 백열등, 가로등 |
| 정보 기술 | 이미지 표시 | TV 화면, 스마트폰 |
| 의료 | 진단, 치료 및 생물학적 관찰 | 광선 치료, 수술용 조명, 현미경 |
| 산업 및 품질 관리 | 검사, 컬러 매칭, 공정 모니터링 | 제품 검사 라인, 색도계, 광학 센서 |
| 예술 및 엔터테인먼트 | 시각 효과 및 색상 렌더링 | 무대 조명, 사진, 영화 |
| 안전 및 신호 | 사람들에게 알림 및 안내 | 신호등, 경고등, 출구 표지판 |
자외선(UV) 및 적외선(IR)
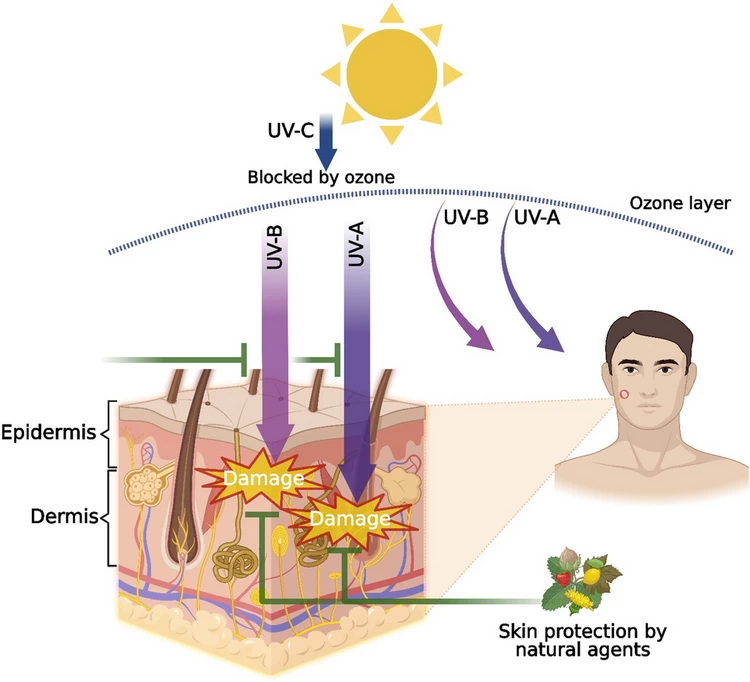
자외선(파장 100~400nm)과 적외선(파장 750nm~1mm)은 가시광선으로 간주되지 않으며 가시광선 스펙트럼에 포함되지 않습니다. 이들의 에너지와 실제 응용 분야는 매우 다릅니다.
자외선(UVA: 315-400nm, UVB: 280-315nm, UVC: 100-280nm)
자외선은 광자 에너지가 높고(3.1-124eV) 화학 결합을 끊을 수 있으며 햇볕에 타는 화상을 유발할 수 있습니다. 일반적으로 소독, 화학 반응, 형광 검출에 사용됩니다.
적외선
가시광선보다 파장이 길지만 광자 에너지가 낮아 열을 방출합니다. 주로 열화상, 야간 투시 장치, 원격 제어 및 통신에 사용됩니다.
| 유형 | 파장 범위 | 주요 기능 및 용도 |
|---|---|---|
| 자외선(UV) | 10-400nm | 높은 에너지; 화학 반응을 일으킴; 살균에 사용됨 자외선 치료, 형광 검출, 산업용 광화학 |
| 적외선(IR) | >750nm 근적외선: 0.75-1.5μm, 중적외선: 1.5-5μm, 원적외선: 5-1000μm | 낮은 에너지, 열 복사, 열화상에 사용됨 야간 투시, 원격 감지, 적외선 통신, 산업용 난방 |
자외선과 적외선은 눈에 보이지 않지만 기술, 의학, 환경 분야에서 대체할 수 없는 중요한 역할을 합니다.
요약
가시광선은 사람의 눈으로 볼 수 있는 파장 범위를 말합니다. 가시광선 스펙트럼의 색은 빨간색에서 보라색까지 연속적이며 우리 생활에서 널리 사용됩니다.
사람들이 자주 묻는 질문
가시광파는 우리에게 무엇을 보여줄까요?
빛은 표면에서 반사되어 우리 눈에 들어와 광수용체에 의해 처리되어 물체를 볼 수 있도록 도와줍니다.
가시광선 중 파장이 가장 짧은 색은 무엇인가요?
가시광선 스펙트럼에서 보라색 빛은 파장이 약 380~450nm로 가장 짧습니다.
가시광선 중 파장이 가장 긴 색은 무엇인가요?
가시광선 스펙트럼에서 적색광은 약 620~750nm 범위로 파장이 가장 깁니다.
가시광선 스펙트럼에는 어떤 색이 있나요?
가시 스펙트럼은 "보라색, 파란색, 청록색, 녹색, 노란색, 주황색, 빨간색"으로 인위적으로 나뉩니다.
엄밀히 말하면 스펙트럼의 색은 경계가 없는 연속적인 색이므로 무한한 수의 색을 포함해야 합니다.
조명 산업에서 가시광선을 응용한 사례에는 어떤 것이 있나요?
- 백색광: 쇼핑몰 조명, 산업용 조명, 스포츠 조명, 가정용 조명, 가로등
- 따뜻한 노란색/주황색 조명: 거실, 식당, 호텔
- 빨간불: 야간 신호등, 무대 조명 및 실외 조명
- 그린 라이트: 신호등, 실내 식물 공간, 병원 및 명상 공간
- RGB 조명: 무대 조명, 건축 장식 및 LED 조명 스트립