目次
トグル概要
照明制御システムは、さまざまな環境において、エネルギー効率、快適性、セキュリティ、生産性を高める上で極めて重要です。これらのシステムには、自動照明システム、調光制御モジュール、遠隔制御照明システムなどがあり、ユーザーはそれぞれのニーズや好みに合った方法で照明を管理することができます。
照明制御システムにはどのような制御が含まれますか?
照明制御システムは、単に照明のオン・オフを切り替えるだけでなく、有線・無線制御を含む幅広い機能を提供する。
- オン/オフ制御:最も基本的な機能で、個々のランプまたはゾーンを制御する。
- 調光:省エネのための連続調光または段階調光。
- 色温度コントロール:ニーズに合わせて暖色または冷色の光量を調節可能。
- RGB/RGBWカラーコントロール:舞台やパフォーマンス用途でよく使われる多色照明。
- 電力制御:照明のエネルギー消費を最適化します。
- シーンコントロール:ワンクリックで異なる照明モードに切り替え。
- センサーコントロール:人感センサーや光センサーで自動的に点灯・消灯。
- リモート/スマートコントロール:有線または無線プロトコル(Wi-Fi、Zigbee、DMX、DALIなど)による集中管理。
| 制御タイプ | 機能 | 申し込み |
|---|---|---|
| オン/オフ | 単一またはグループ照明の切り替え | 基本的な家庭用およびオフィス用 |
| 調光 | 連続または段階的に明るさを調整 | 省エネ、ムード照明 |
| CCTコントロール | 温白色から冷白色への光の変更 | 職場と家庭の快適性 |
| カラーコントロール | RGB/RGBWフルカラーをコントロール | ステージ、イベント、店舗ディスプレイ |
| 電源管理 | エネルギー使用の監視と削減 | 大型ビル、工業 |
| シーン設定 | 様々なニーズに対応するプリセット・モード | 会議、映画館、展覧会 |
| センサーコントロール | モーション/ライトセンサーによる自動制御 | スマートビル、省エネ |
| スマート/リモート | アプリ、ワイヤレス、セントラルシステムによる制御 | スマートホーム、モダンオフィス |
照明制御システムとエネルギー効率
照明制御システムの最も大きなメリットのひとつは、エネルギー効率を高めることができる点です。自動照明システムや調光制御モジュールのような様々な技術を使用することで、エネルギー消費を大幅に削減することができます。
産業用および業務用LED照明を製造しており、すべてスマート制御システムを備えています。以下のことが可能です。 全製品を見る 範囲または お問い合わせ.
| 照明制御システム | 省エネルギー(%) | 説明 |
|---|---|---|
| 自動照明システム | 30-50% | 使用状況に応じて自動的に照明をオン/オフし、無駄な使用を削減。 稼働率が変動するエリアでは重要なカギとなる。 |
| 調光制御モジュール | 10-30% | 周囲の明るさやユーザーの好みに応じて光量を調整。 特に自然光が変化する環境では効果的だ。 |
| タイムクロック照明制御 | 15-35% | 特定の時間帯だけ照明が作動するようにスケジュールし、時間外の使用量を減らす。 商業施設では一般的。 |
| デイライト・コントロール | 20-40% | 自然光を利用し、人工照明を減らす。 最大限の効率を得るために、調光制御モジュールと組み合わせることが多い。 |
| リモコン照明システム | 5-15% | 離れた場所から照明をコントロールでき、必要な時だけ照明を点灯させることができる。 広大な敷地に最適。 |
ライティング・コントロール・モジュールとは?
照明制御モジュールは照明制御システムの中核部品で、主にさまざまな照明機能の管理と調整を担当する。
照明制御モジュールは、照明システム内に設置され、照明器具を制御システムに接続する「制御ユニット」である。
端的に言えば、だ:
照明制御モジュールなしでは、スマート照明システムは集中管理と自動化を実現できない。
- 調光モジュール:明るさ調整用に特別に設計。
- リレーモジュール:単純にランプのオン/オフ機能を制御する。
- マルチチャンネル制御モジュール:スイッチング、調光、色温度、電源制御など複数の機能を統合。
- ワイヤレス・コントロール・モジュール:Zigbee、Wi-Fi、Bluetoothを内蔵しており、スマートホームの照明制御システムに適しています。
スイッチ・コントロール・モジュール
| スイッチ・コントロール・モジュールのタイプ | 制御ループ数 | 定格電力 (A) | 申し込み |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4ウェイ・スイッチ・コントロール・モジュール | 4 | 10A | 少数の照明を制御する必要がある小規模な住宅用または商業用アプリケーションに適しています。 |
| 8ウェイ・スイッチ・コントロール・モジュール | 8 | 16A | より広範な制御を必要とする中規模スペースに最適。 |
| 16ウェイ・スイッチ・コントロール・モジュール | 16 | 32A | 複数の照明を同時に管理する必要がある大規模な商業施設や産業施設で使用されます。 |
調光制御モジュール
| 調光技術 | 制御方法 | 申し込み | メリット |
|---|---|---|---|
| サイリスタ調光 | 位相制御 | 白熱灯やハロゲン灯の調光用として、一般家庭で使用されている。 | ちらつきを抑えたスムーズな調光。一般家庭に標準装備。 |
| PWM(パルス幅変調) | デジタル制御 | 正確な調光のためにLED照明制御システムで広く使用されています。 | 高精度とエネルギー効率を提供。商業用途に最適。 |
| 0-10V調光 | アナログ制御 | 蛍光灯やLED照明の調光用として、商業施設では標準的に使用されている。 | 広いエリアで安定した調光を実現。オフィスや工業スペースで一般的。 |
| RES(抵抗調光) | 抵抗制御 | 抵抗調光を必要とする特定の照明に使用される。 | 古い照明技術との互換性を確保。一般的ではないが、レガシーシステムには不可欠。 |
有線制御方式
| 有線制御方式 | 送信信号 | 申し込み |
|---|---|---|
| DALI | デジタル | 正確な制御と信頼性が最優先される業務用照明制御システムに使用。 |
| DMX512 | デジタル | 舞台照明やハイエンドの建築照明でよく使われ、複雑なシーンや効果を管理する必要がある。 |
| RS485 | デジタル | 堅牢な長距離通信が必要な産業環境に適用。 |
ワイヤレス制御方式
| ワイヤレス制御方式 | 送信信号 | 申し込み |
|---|---|---|
| ブルートゥース | デジタル | 1つの部屋の数個の照明を制御するなど、住宅環境での短距離制御に最適。 |
| Wi-Fi | デジタル | スマートホームアプリケーションに最適で、インターネットに接続できる場所ならどこからでも照明を遠隔操作できる。 |
| ジグビー | メッシュネットワーク | 商業ビルのスマート照明制御システムなど、複数のデバイスをネットワーク接続する必要がある大規模システムで使用される。 |
モーション・センサー・モジュール
センサー・コントロール・モジュールは、自動照明システムに不可欠なもので、動き、周囲の明るさ、時刻などの環境条件に基づいて照明を点灯または消灯することができます。
| センサータイプ | 制御原理 | 申し込み | メリット |
|---|---|---|---|
| PIR(パッシブ赤外線) | 赤外線検出 | 住宅や小規模な商業施設では一般的で、動体検知によって照明を作動させる必要がある。 | 低消費電力で狭いエリアでも確実に検知。ホームオートメーションに最適。 |
| マイクロ波センサー | ドップラー効果 | 長距離検知が必要な倉庫や産業現場のような広いスペースに適しています。 | 障害物を貫通し、より広い検知範囲を提供。広いオープンスペースで効果的。 |
| タッチ・コントロール・モジュール | 容量センシング | 洗練されたユーザーフレンドリーなインターフェイスを備えた最新のスマート照明システムに使用され、多くの場合、高級住宅および商業用アプリケーションで使用されている。 | 最小限の操作で直感的なコントロールが可能。高級住宅やオフィスで人気。 |
スマート照明制御システムのシナリオ比較
現在、スマート照明制御システムはほとんどのシナリオに組み込まれているが、シナリオによって照明制御の要件と実装方法は大きく異なる。
- 産業用:安定性、エネルギー効率、安全性を優先し、主に有線制御に頼る。
- 商用:エネルギー効率とユーザーエクスペリエンスの両方を達成するためには、多くの場合、ハイブリッドシステムが利用される。
- ホーム利便性とユーザー体験を優先し、主にワイヤレス・スマート・コントロール(アプリ、音声、オートメーション)を活用。
| シナリオ | 主な目的 | コントロール機能 | テクノロジー | 例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| インダストリアル | 省エネ、安全性 | スケジューリング、センサー、ゾーニング調光 | 有線(DALI、0-10V、KNX) | 工場、倉庫、 ハイベイ照明 |
| コマーシャル | 省エネ、ユーザーエクスペリエンス | 調光、色温度、シーン切り替え | ハイブリッド(有線+無線)、DALI+Zigbee/Wi-Fi | オフィス、ホテル、モール |
| ホーム | 快適性、利便性 | アプリ/音声、RGB、調光 | ワイヤレス(Wi-Fi、Zigbee) | 住宅、アパート |
セキュリティと利便性
また、照明制御システムは、自動点灯、遠隔操作、プログラム可能な照明など、さまざまな機能によってセキュリティと利便性を向上させる。
| 特徴 | セキュリティ強化 | 利便性の向上 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 自動照明システム | 高い | 高い | 動きを感知すると自動的にライトが点灯し、侵入者を抑止し、暗い場所での利便性を高めます。このようなシーンで活躍します。 |
| リモコン照明 | ミディアム | 高い | ユーザーが照明を遠隔操作できるため、利便性が向上し、潜在的なセキュリティ脅威への迅速な対応が可能になる。 |
| プログラマブル照明システム | ミディアム | ミディアム | 照明のスケジューリングが可能で、占有されていなくても占有されているように見せることでセキュリティを提供する。タイムロック制御がよく使われる。 |
| センサーライト制御 | 高い | ミディアム | 動きが検知されるとライトが点灯し、セキュリティが強化され、ハンズフリーの照明ソリューションが提供されます。セキュリティシステムには欠かせません。 |
LedrhythmのGOLDENシリーズLEDのufoの高い湾ライトマイクロウェーブセンサー:
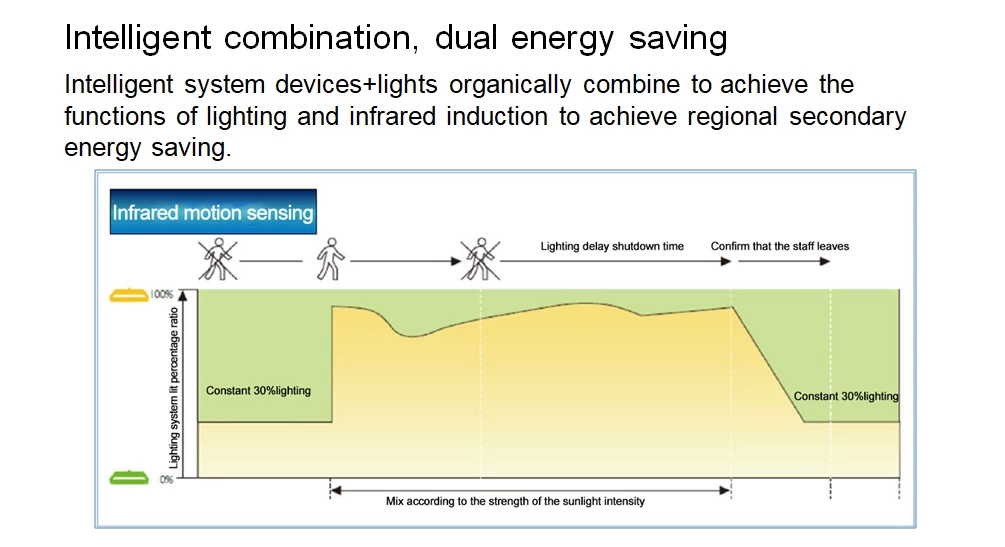
GOLDENシリーズはマイクロ波制御モジュールを例として、一つのランプを制御します。Zigbee信号マイクロ波センサー制御モジュールは、Tuya制御プラットフォームを搭載し、ランプの調光、スイッチング、グループ化、グループ制御などを実現します。
- 十分な明るさがあり(調光優先機能)、実際の明るさが設定した明るさのしきい値以上であれば、通行人の有無にかかわらず消灯する。
- 薄暗くなり、実際の明るさが設定した閾値以下になると、人が通り過ぎ、ランプが点灯する。
- 100%の明るさを維持し、一定時間遅延させます。遅延時間を設定できます。
- ディレイタイムが終了したら、待ち時間を入力します。時間と明るさを設定できます。
- 遅延時間が終了するとランプが消灯する。


結論
結論として、照明制御システムの原理と効果は、エネルギー効率、快適性、生産性、安全性、および利便性の向上における照明制御システムの重要な役割を示している。スイッチ制御、調光、センサーベースの方法など、さまざまな照明制御モジュールを統合することで、住宅と商業空間の多様なニーズを満たすオーダーメイドのソリューションが可能になります。
人々はこうも尋ねる
スマート照明コントロール・システムはLEDにしか対応していないのですか?
スマート照明制御システムはLEDに限ったものではない。蛍光灯や白熱灯にも使用できるが、互換性、エネルギー効率、寿命、機能性において大きな利点があるLEDは、照明制御システムに最も適している。
人感センサー照明は、スマート照明制御システムに属しますか?
モーションセンサー照明は自動化を可能にし、他の照明制御と組み合わせることができるからです。
照明制御システムは有線と無線どちらが良いのか?
有線か無線かの選択は、主にアプリケーションのシナリオ、要件、設置コスト、拡張性によって決まる。絶対的な「ベスト」はなく、それぞれに長所と短所があります。