Índice
AlternarIntrodução
Watts, lúmens, candela e lux são três desses termos que são essenciais quando se consideram soluções de iluminação modernas, especialmente com o aumento da tecnologia LED. Compreender a iluminação pode ser uma tarefa complexa devido aos vários termos e métricas utilizados para descrever diferentes aspectos da luz. Este artigo irá aprofundar as definições destes termos, explicando o que significam, como se relacionam entre si e como fazer a conversão entre eles.
O que é um Watt num aparelho de iluminação?
Os watts medem a quantidade de energia eléctrica consumida por uma fonte de luz. Quanto maior for a potência, maior será o consumo de energia.
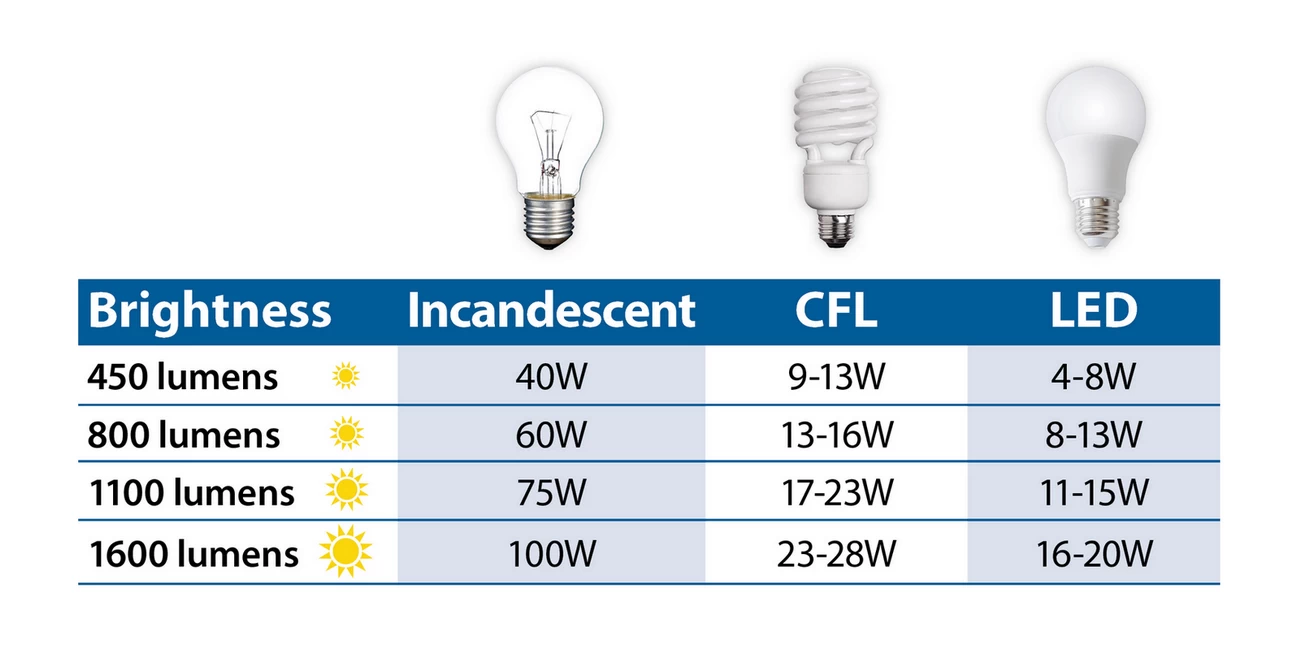
Historicamente, uma potência mais elevada estava associada a uma luz mais brilhante, especialmente nas lâmpadas incandescentes. No entanto, com os avanços nos LEDs, os watts já não indicam diretamente o brilho. Por exemplo, uma lâmpada LED de 10 watts pode produzir a mesma quantidade de luz que uma lâmpada incandescente de 60 watts.
- Consumo de eletricidade por hora (kWh) = Potência (W) × 0,001
Definição do lúmen
Lúmen (abreviado lm) é a unidade de fluxo luminoso. Os lúmenes medem a quantidade total de luz visível emitida por uma fonte de luz. Quanto mais elevado for o número de lúmenes, mais luz visível a luz liberta e mais brilhante parece. Os lúmens e os watts são frequentemente convertidos entre si com base na eficácia luminosa (lm/W).
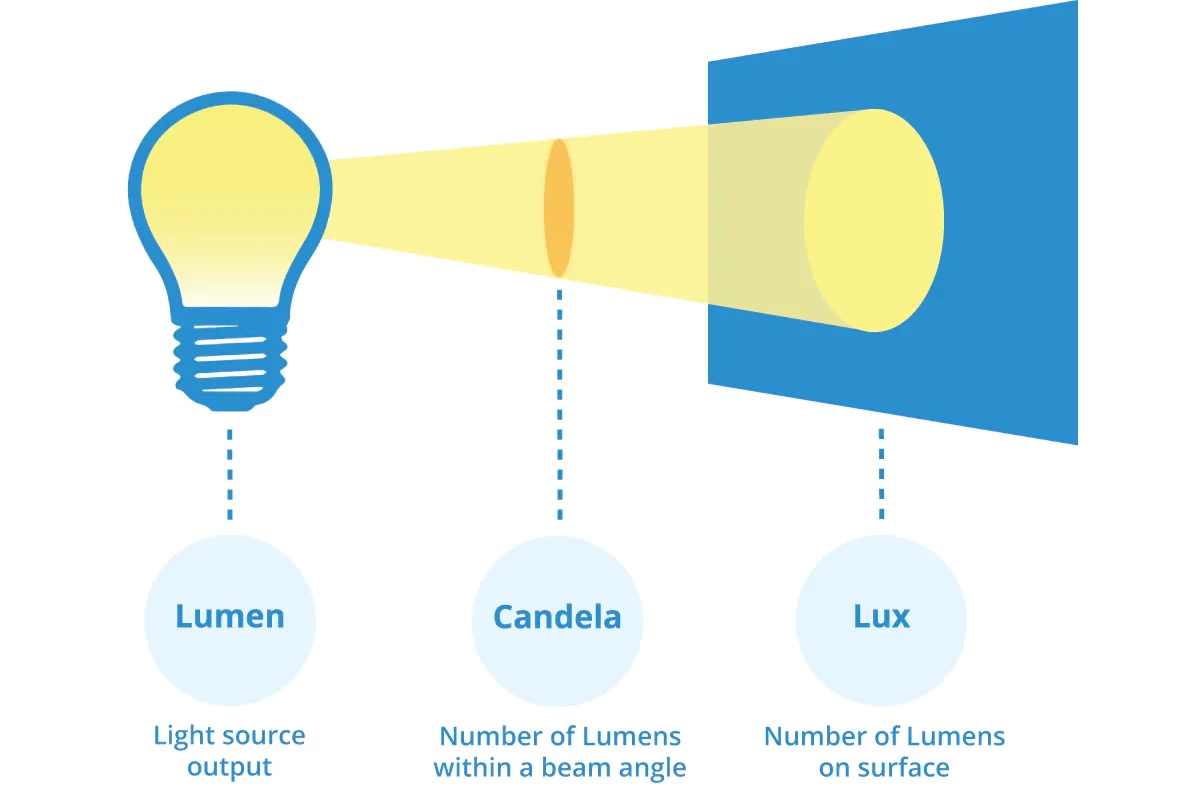
- Os lúmenes representam a quantidade total de luz emitida por uma lâmpada, independentemente da direção.
Definição de Lux
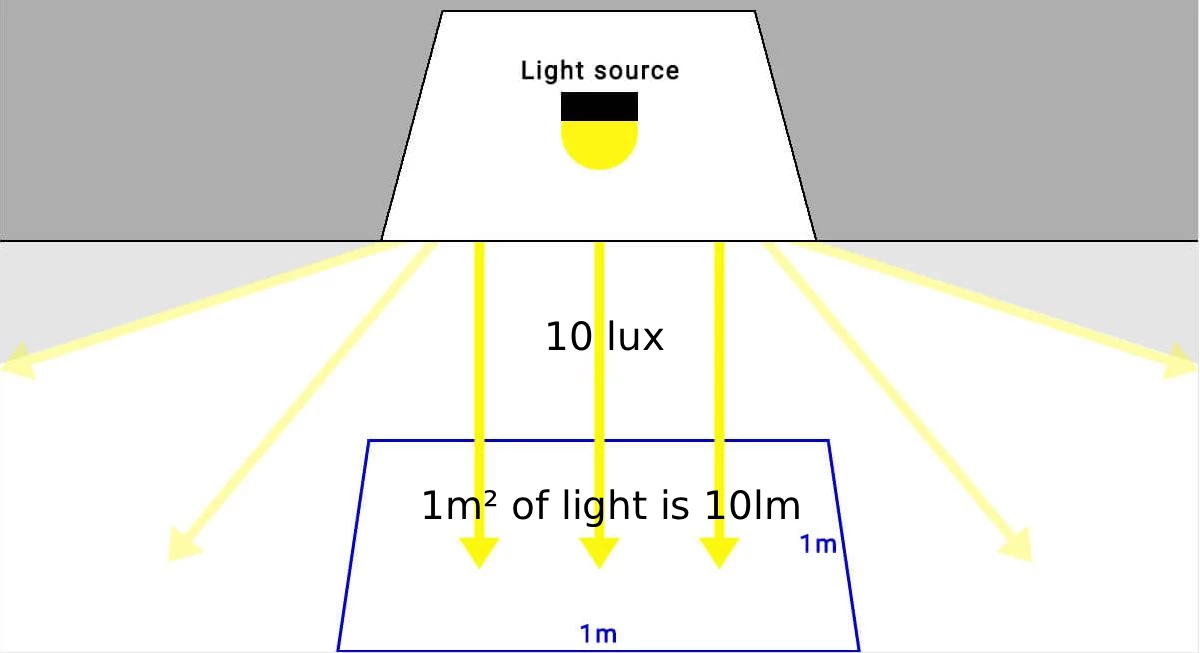
Lux é uma medida de iluminância, que representa a quantidade de luz que atinge uma área específica. Um lux equivale a um lúmen por metro quadrado. Enquanto os lúmenes indicam a quantidade de luz que uma fonte emite, o lux indica a quantidade de luz que efetivamente atinge e ilumina uma superfície.
Quanto mais elevado for o Lux, mais brilhante é a superfície iluminada. Para luzes com a mesma potência e lúmenes, quanto maior for a altura de instalação, menor será a iluminação da superfície (lux).
- Iluminação da garagem: 100 lux é suficiente, o que significa 100 lúmenes de luz por metro quadrado.
- Fábrica ou armazém: São necessários 500 lux, o que significa 500 lm de luz por metro quadrado.
Candela Significado
A candela (símbolo cd) é uma unidade de intensidade luminosa, utilizada para expressar a quantidade de luz emitida por uma fonte luminosa numa direção específica. Quanto mais concentrada estiver a luz numa direção, maior será o valor da candela; quanto mais dispersa estiver a luz, menor será o valor da candela.
Por exemplo, se uma luz brilha diretamente para a frente, a luz está mais concentrada na direção diretamente à frente da luz, pelo que a candela é a mais elevada, enquanto a candela será mais baixa na direção lateral.
- Lanterna: A intensidade da luz é maior na parte da frente e pode iluminar mais longe.
- Candeeiro de secretária: A luz é dispersa, com baixa candela em todas as direcções.
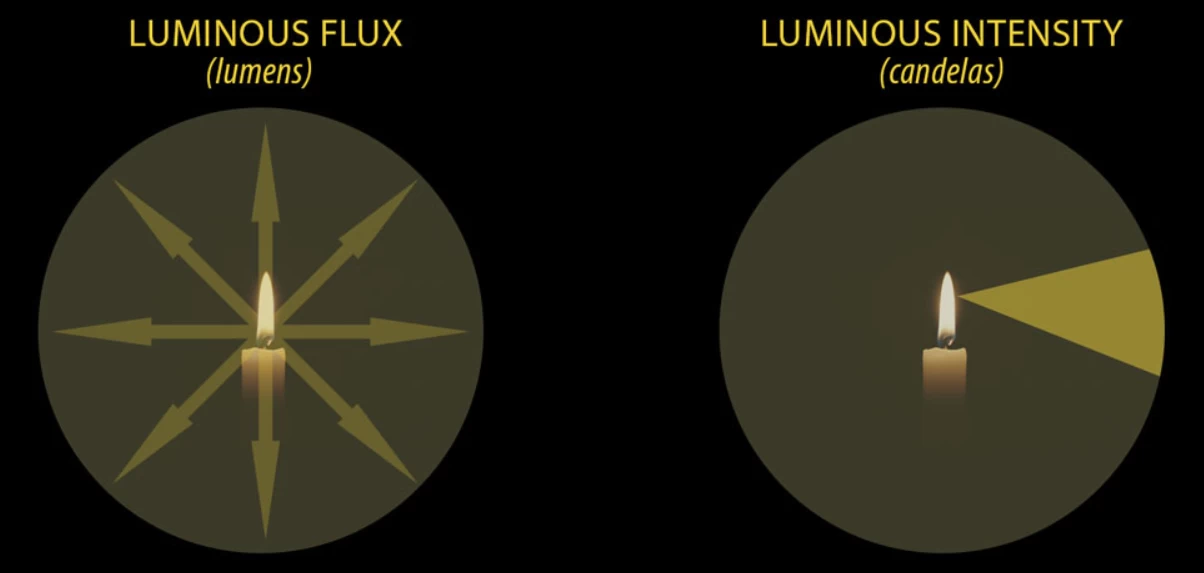
Candela vs Lumens
A candela (cd) e o lúmen (lm) são unidades fundamentais da física na ótica, mas as suas definições fundamentais são completamente diferentes.
- O lúmen descreve a quantidade total de luz visível emitida por uma fonte de luz em todas as direcções.
- A candela descreve a intensidade luminosa de uma fonte de luz numa direção específica.

| Tipo de fonte de luz | Candela (cd) Significado | Lúmen (lm) Significado |
|---|---|---|
| Apontador laser | Chave (a luz é altamente concentrada, o valor de cd é muito elevado) | Secundário (a produção total de luz pode ser muito pequena) |
| Farol para automóvel | Importante (determina a distância do feixe e a luminosidade central) | Importante (o fluxo luminoso total afecta a cobertura da iluminação) |
| Lâmpada de interior | Poucas vezes utilizado | Núcleo (determina a luminosidade geral da divisão) |
Nota: Não é possível efetuar a conversão de Candela para Lúmen. É necessário conhecer o ângulo do feixe da fonte de luz (ângulo sólido). Por exemplo:
- Uma fonte de luz de 100 cd com um feixe estreito (10°) produzirá menos lúmenes totais.
- Uma fonte de luz de 100 cd com um ângulo amplo (120°) produzirá mais lúmenes totais.
Converter Lumens em Watts
A conversão de watts em lúmens varia muito, dependendo da eficácia luminosa (lm/W) da luz. Diferentes tipos de fontes de luz (incandescente, halogénea, fluorescente, LED) e diferentes marcas e modelos da mesma fonte de luz têm diferentes eficácias luminosas.
Assim, basta conhecer a eficácia luminosa (lm/W) da luz para efetuar a conversão entre lúmens e watts.
- Calculadora de lúmens para watts :Watts = Lúmens ÷ Eficácia luminosa (lm/W)
- Calculadora de Watts para Lúmens :Lúmens = Watts × Eficácia Luminosa (lm/W)
Gráfico de conversão de lúmens para watts Exemplo: A eficiência luminosa é de 100lm/W
| Lúmens (lm) | Lumens para Watts | Watts (W) |
|---|---|---|
| 800lm | Lumens (lm) ÷ 100 lm/W | 8W |
| 1000lm | 10W | |
| 1500lm | 15W | |
| 5000lm | 50W | |
| 10000lm | 100W |
Esta tabela de conversão é apenas um exemplo. Pode calculá-la com base na eficiência luminosa real da sua lâmpada.
Converter Lux em Lumens
O lúmen indica a quantidade total de luz visível emitida e o lux indica quantos lúmenes de luz são recebidos por um metro quadrado de superfície.
Por conseguinte, ao converter lux em lúmens, é necessário conhecer a área da superfície iluminada! O lux é uma unidade de densidade relacionada com a área e não pode ser convertido em lúmens sem ter em conta a área.
Converter lux em lúmens ou calculadora de lúmens em lux:
- Lúmen (lm) = Lux (lx) × Área (㎡)
- Lux (lx) = Lúmen (lm) ÷ Área (㎡)
Converter lux em passos de lúmens:
- Utilize um luxímetro para medir a iluminância (lx) da superfície iluminada (tampo da mesa, chão). Por exemplo, 500 lux.
- Medir o comprimento e a largura da área e calcular a área: Área = Comprimento (m) × Largura (m).Por exemplo, 2 ㎡.
- Calcular os lúmens: 1000 (lm) = 500(lux) × 2(㎡).
| Objetivo | Área | Converter | Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
| A iluminação da superfície da secretária atinge 500 lux | 0.72 ㎡ | 500 lux × 0,72 ㎡ = 360 lm | São necessárias luzes com um fluxo luminoso ≥ 360 lm. |
| Verificar se as luzes do quarto são suficientemente brilhantes Luminária 1000lm | 12 ㎡ | 1000 lm ÷ 12 ㎡ ≈ 83 lx | Iluminação inferior à recomendada para a sala são necessárias fontes de luz adicionais! |
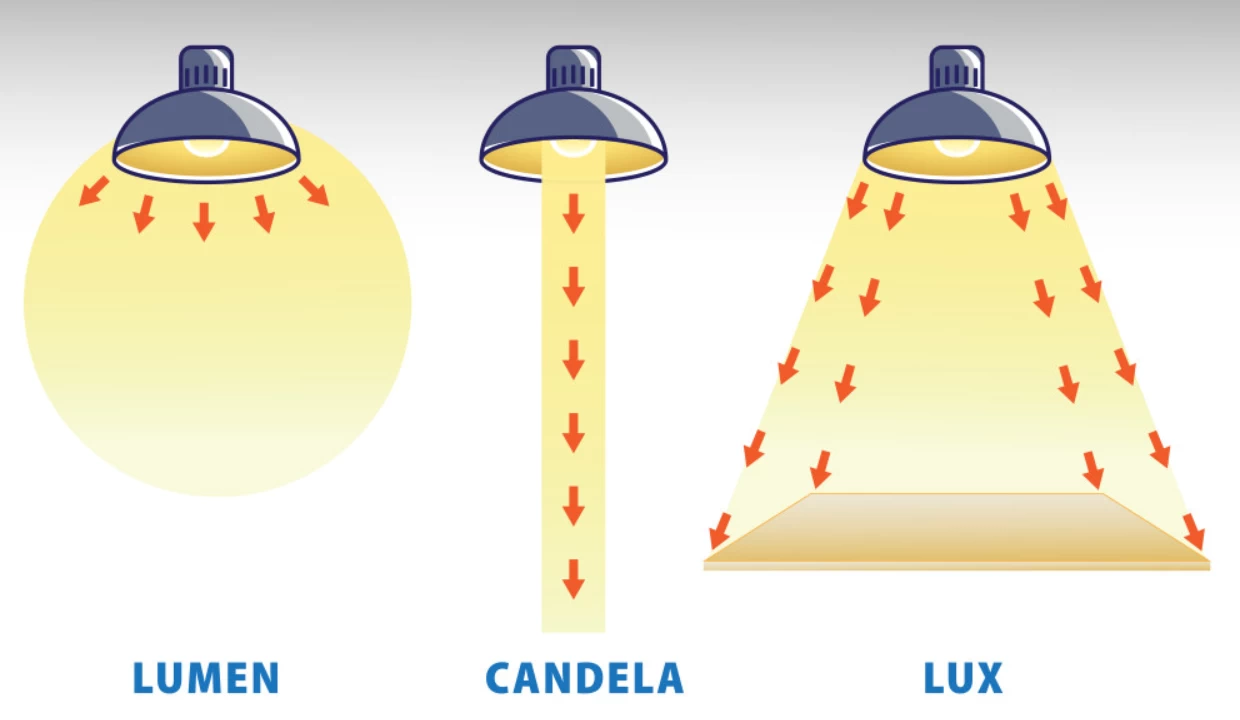
Lúmen vs Candela vs Lux
| Conceito | Definição | Unidade | Caraterísticas principais | Exemplo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluxo luminoso | Quantidade total de luz emitida por uma fonte | Lúmen (lm) | Sublinha o "montante total", independentemente da direção | Uma lâmpada que emite toda a sua luz |
| Intensidade luminosa | Intensidade da luz numa direção específica | Candela (cd) | Dá ênfase à "direccionalidade", ao grau de concentração da luz | Feixe de luz da lanterna |
| Iluminação | Grau de iluminação de uma superfície | Lux (lx) | Dá ênfase ao "objeto iluminado", à luz por unidade de área | Luminosidade numa secretária |
Resumir
Em conclusão, compreender a relação entre lux, lúmens, watts e outros termos de iluminação é fundamental para tomar decisões sobre soluções de iluminação industrial e comercial. Quando confrontadas com diferentes locais ou necessidades de iluminação, estas unidades diferem no tipo e na instalação das luzes.
As pessoas também perguntam
Quantos lúmenes tem uma lâmpada de 100 watts?
Não existe uma relação de conversão fixa entre watts e lúmens; é necessário determinar a eficácia luminosa (lm/W).
- 100W incandescente (12-16 lm/W): 1200-1600 lm
- 100W CFL (50-60 lm/W): 5000-6000 lm
- 100W LED (80-100 lm/W): 8000-10000 lm
Quanto maior for a potência, maior será o valor do lúmen?
Em termos estritos, uma potência mais elevada não significa necessariamente mais lúmenes. A relação entre os dois depende da eficácia luminosa (lm/W) da fonte de luz.
- Diferentes tipos de lâmpadas:
Lâmpada incandescente de 100W → 1500 lm; LED de 20W → 1800 lm - O mesmo tipo de lâmpada:
100W LED (80 lm/W) → 8000 lm; 80W LED (130 lm/W) → 10400 lm
Quanto maior for o valor do lúmen, maior será o lux?
Não necessariamente. Se os lúmenes emitidos por uma fonte de luz aumentarem, mas a área de distribuição da luz também aumentar, o valor lux pode permanecer o mesmo ou até diminuir.
Por exemplo, diferentes ângulos de feixe e diferentes alturas de montagem da mesma luz afectarão a área de cobertura da luz.
Que fator determina o valor da candela?
O valor da candela (cd) é normalmente determinado pelo fluxo luminoso e pelo ângulo luminoso. Quanto maior for o fluxo luminoso e menor for o ângulo do feixe, maior será a candela.
O máximo de lux é melhor?
Claro que não. Diferentes cenários têm intervalos de lux recomendados. Uma luz demasiado alta ou demasiado baixa afectará a experiência de iluminação.
Uma luminosidade demasiado elevada pode causar encandeamento, encandeamento, fadiga e até riscos para a segurança. Se se tratar de um bloco operatório ou de uma fábrica, uma luminosidade mais elevada pode garantir eficiência e segurança.








