Como funciona a regulação da intensidade luminosa dos LED - iluminação exterior e interior
Regulação da intensidade luminosa dos LEDs é um aspeto crítico dos sistemas de iluminação modernos, especialmente em ambientes industriais como fábricas, portose estádiosonde as necessidades de iluminação podem variar significativamente. Compreender como Luzes LED reguláveis e as diferentes tecnologias envolvidas é fundamental para otimizar o consumo de energia, melhorar a qualidade da luz e prolongar a vida útil dos aparelhos de iluminação.
O que é Escurecimento?
Escurecimento refere-se ao processo de ajustamento do luminosidade das luzes LED para satisfazer várias necessidades de iluminação. Ao reduzir ou aumentar o fluxo luminoso da fonte de luz, é possível adaptar o ambiente de iluminação a diferentes aplicações. A capacidade de luzes LED fracas é crucial em ambientes como fábricas, armazéns e estádios desportivos, onde os níveis de iluminação têm de ser ajustados em função da eficiência ou do ambiente.
Luzes LED com regulação de intensidade: Métodos e tecnologias
Escurecimento de luzes LED pode ser conseguido através de vários métodos. Cada método tem aplicações específicas, dependendo do ambiente e do controlo de iluminação pretendido. Em ambientes industriais como portos ou estádios, é necessário um controlo fiável e eficiente da sistemas de regulação da intensidade luminosa para luzes LED são essenciais para a iluminação interior e exterior.
1. escurecimento PWM (modulação da largura de pulso)
O Método de regulação PWM converte um sinal analógico num sinal digital através do controlo do ciclo de funcionamento da onda quadrada, que ajusta a corrente no circuito. Ao variar os tempos de "ligado" e "desligado" do sinal, pode reduzir a quantidade de corrente que chega à luz, obtendo um funcionamento suave e eficiente. regulação da intensidade luminosa.
2. regulação da tensão
Trata-se de ajustar o tensão fornecido à luz. Em Sistemas de iluminação LEDEspecialmente nas fontes de alimentação com inversor de meia ponte, a regulação da intensidade luminosa é conseguida através do controlo da tensão CC. Isto altera a corrente da lâmpada, resultando numa redução da emissão de luz e num efeito de regulação da intensidade luminosa.
3. escurecimento por modulação de frequência de impulsos
Este método altera a frequência de funcionamento do balastro. Ao aumentar a resistência do indutor do balastro, reduz a corrente total. Este método é frequentemente utilizado em sistemas de iluminação fluorescente, mas pode ser aplicado a Regulação da intensidade luminosa dos LEDs para obter resultados semelhantes.
4. regulação de intensidade controlada por fase
O controlo de fase é um método amplamente utilizado para regulação da intensidade luminosa lâmpadas incandescentes e também pode ser aplicado a Luzes LED. A tiristor é utilizado para controlar o ângulo de fase do sinal CA, baixando efetivamente a tensão de saída. Isto permite um controlo preciso do nível de brilho da luz.
5. escurecimento por corrente constante
O método de regulação de corrente constante envolve o ajuste da corrente que flui através da luz. Ao regular a corrente com controlo analógico, é possível controlar eficazmente a luminosidade da Luzes LEDque ajuda a manter uma saída de luz consistente, mesmo quando a luminosidade muda.
6. escurecimento resistivo
Neste método, é colocada uma resistência variável em série com a luz. Ao ajustar a resistência, a corrente diminui, levando a uma redução do brilho. Embora este não seja o método mais eficiente para Regulação da intensidade luminosa dos LEDsO sistema é simples e eficaz em determinadas aplicações.
7. escurecimento escalonado
Este método é simples: ao alternar o interrutor de alimentação num padrão específico, é possível obter vários níveis de luminosidade. Este método é normalmente utilizado em Iluminação LED luminárias para espaços comerciais e industriais que não requerem regulação de intensidade luminosa infinitamente variável.
8. escurecimento analógico
Neste método, a luminosidade do LED é ajustado através da modificação do sinal de tensão utilizando um controlo analógico. A regulação analógica é precisa e eficaz, mas pode por vezes conduzir a uma saída de luz inconsistente em comparação com métodos digitais mais modernos, como PWM.
Tabela: Comparação de tecnologias comuns de escurecimento de LEDs
|
Método de escurecimento |
Aplicação |
Vantagens |
Desafios |
|
Dimerização PWM |
Iluminação industrial e exterior |
Controlo preciso, eficiência energética |
Pode causar cintilação a níveis de regulação de intensidade baixos |
|
Regulação de intensidade controlada por fase |
Aplicações de alta potência (estádios) |
Simples e económico |
Nem sempre compatível com todos Luzes LED |
|
Escurecimento 0-10V |
Fábricas, portos |
Regulação suave da intensidade luminosa, fiável |
Requer cablagem especializada |
|
Dimerização DALI |
Aplicações comerciais e industriais |
Controlo escalável e inteligente |
Configuração complexa |
As lâmpadas LED utilizam atualmente fontes de alimentação comutadas. Podem ser reguladas utilizando métodos como a regulação por tiristores, PWM, 0-10V (regulação linear), DAIL e DMX512.
Como é que um Dimmer LED Trabalhar?
Compreensão como funcionam os reguladores de intensidade luminosa LED é essencial para a criação de uma sistema de regulação da intensidade luminosa para LEDs em ambientes industriais. Interruptores com regulação de intensidade LED controlar a quantidade de corrente que flui para a luz, ajustando os níveis de luminosidade de acordo com a entrada definida. A capacidade de luzes LED fracas não só cria flexibilidade como também melhora a eficiência energética, especialmente em ambientes com necessidades de iluminação variáveis, como estádios e armazéns.
Todas as luzes LED são reguláveis?
Nem todos Luzes LED são criados iguais quando se trata de regulação da intensidade luminosa. A questão, "Todas as luzes LED são reguláveis??" é comum quando se pensa em atualizar a iluminação em ambientes comerciais ou industriais. A resposta depende do Regulador de luz LED e o específico Luminárias LED em utilização. Por exemplo, Ritmo LEDcomo os seus produtos luzes LED de alto brilho e luminárias LED à prova de vaporsão especificamente concebidos para aplicações reguláveis em ambientes interiores e exteriores.
Luzes LED reguláveis: Vantagens
-
Poupança de energia: Ao reduzir a luminosidade do Luzes LEDpode obter poupanças de energia significativas, especialmente em grandes ambientes industriais como portos e fábricas.
-
Vida útil prolongada: Escurecimento reduz a tensão sobre Controladores LEDprolongando a vida útil dos aparelhos.
-
Personalização: Luzes LED reguláveis oferecem mais controlo sobre o ambiente de iluminação, seja em estádios, fábricas, ou edifícios comerciais.
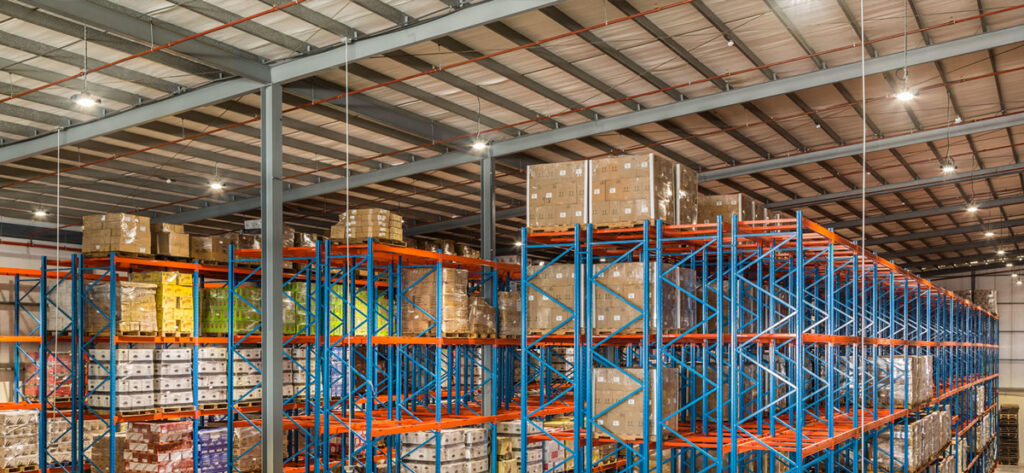
Iluminação LED com regulação de fluxo luminoso em aplicações industriais e comerciais
A capacidade de iluminação LED fraca tem um impacto profundo no consumo de energia e na eficiência operacional, particularmente em ambientes industriais e comerciais como fábricas, portose estádios. Implementação de um sistema de regulação da intensidade luminosa para LEDs pode reduzir significativamente os custos de energia, mantendo as condições de iluminação óptimas.
1. Iluminação LED de alto brilho
Em ambientes industriais, como armazéns e fábricas, Iluminação LED de alto brilho os aparelhos devem ser reguláveis para se adaptarem a diferentes tarefas e actividades. Luzes LED de alto brilho da LED Rhythm são concebidos para funcionar com uma vasta gama de reguladores de intensidade luminosa, oferecendo flexibilidade em grandes espaços.
2. Iluminação LED de baía baixa
Para áreas que requerem níveis mais baixos de luz, tais como salas de armazenamento ou garagens comerciais, luzes LED de baía baixa e Luminárias LED de baixo brilho oferecem a solução ideal com regulação da intensidade luminosa. Estas luzes proporcionam uma cobertura uniforme e podem ser reguladas de acordo com as necessidades específicas do ambiente.
3. Projectores e iluminação exterior
Iluminação exterior LED, especialmente em estádios e portospode também beneficiar de regulação da intensidade luminosa capacidades. Projectores reguláveis permitem ajustar os níveis de luz durante diferentes eventos ou alturas do dia, garantindo a utilização mais eficiente da energia.
Problemas comuns com Luzes LED com regulação de intensidade
Enquanto Regulação da intensidade luminosa dos LEDs oferece inúmeras vantagens, é essencial compreender os problemas comuns que podem surgir:
-
Cintilação: Má qualidade Reguladores de intensidade luminosa LED ou sistemas incompatíveis podem fazer com que as luzes cintilem quando reguladas.
-
Zumbido: Alguns Luzes LED pode produzir um zumbido quando utilizado com interruptores com regulação da intensidade da luz.
-
Limites de escurecimento: Nem todos Luzes LED podem ser regulados para níveis extremamente baixos sem problemas. Compreender os limites da sua Sistema de regulação LED é fundamental.
Do ponto de vista das aplicações de regulação da intensidade luminosa: controlo com fios e controlo sem fios
O controlo de regulação da intensidade da luz com fios tem um sinal estável e fiável. O controlo de regulação da intensidade da luz sem fios é fácil de instalar, mas sofre facilmente interferências e tem pouca estabilidade.
Método de controlo da intensidade luminosa com fios.
![]()
Método de controlo de regulação da intensidade luminosa sem fios. Os protocolos comuns de transmissão de sinal incluem os protocolos Zigbee, Bluetooth e WiFi.

Produtos de regulação de fluxo luminoso da Ledrhythm
Ritmo LED oferece uma gama de soluções de iluminação regulável para aplicações industriais e comerciais, incluindo
-
LED Rhythm High Bay LED
-
LED Rhythm Vapor Tight LED
-
Fita LED Rhythm regulável
Entre os produtos da Ledrhythm, os candeeiros de rua, os projectores, os candeeiros para minas, os candeeiros à prova de triagem, etc., têm todos soluções de regulação da intensidade luminosa. Clique aqui para obter mais informações
Os candeeiros de rua Ledrhythm, os candeeiros industriais e mineiros, etc., utilizam sensores de micro-ondas e sensores de luz para conseguir o controlo da intensidade luminosa. O efeito de regulação da intensidade luminosa é apresentado na figura.
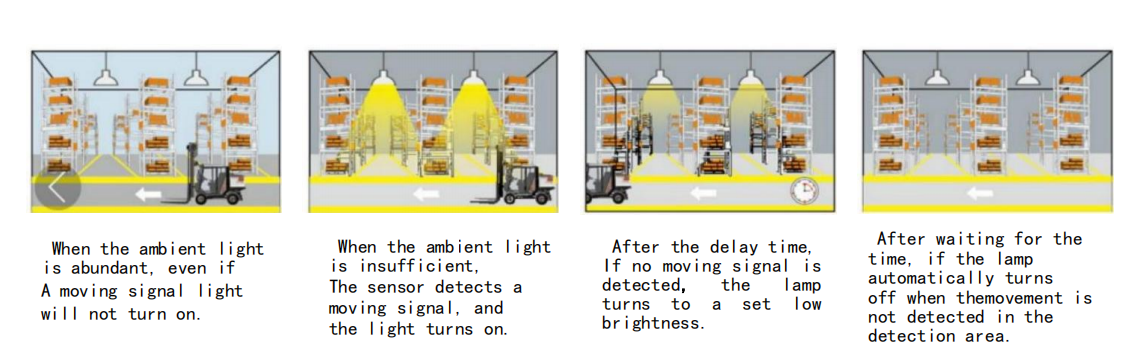
Pode controlar luzes de rua, projectores e candeeiros de mineração utilizando dispositivos centralizados com fios ou controlo sem fios através de uma aplicação. Isto permite ajustar o tempo de escurecimento, o efeito e o agrupamento das luzes.
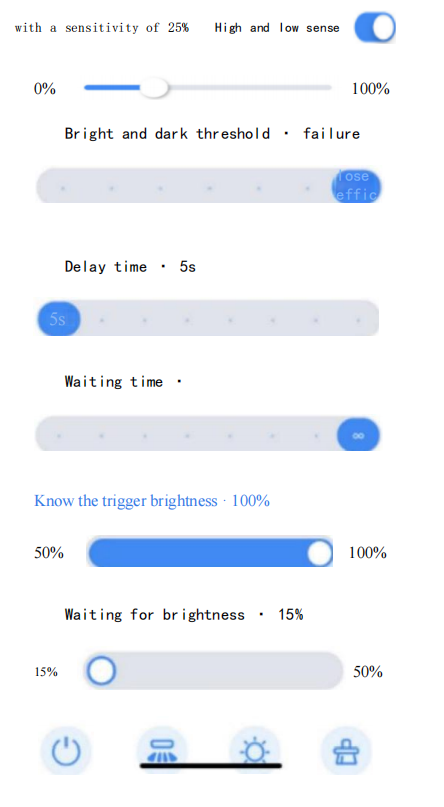
Conclusão: O futuro da Luzes LED com regulação de intensidade em Aplicações industriais
O futuro da Luzes LED reguláveis reside em sistemas mais inteligentes e integrados que podem ser controlados remotamente ou através de sistemas automatizados. Em ambientes industriais como fábricas, portose estádios, a possibilidade de personalizar os níveis de iluminação com sistemas LED reguláveis está a tornar-se cada vez mais vital para melhorar a eficiência energética e a flexibilidade operacional.
LED Rhythm's produtos avançados com regulação de fluxo luminoso, tais como os seus baía alta e estanque ao vapor são líderes no fornecimento de soluções de iluminação personalizáveis e energeticamente eficientes para aplicações industriais em grande escala.









